Ocular Involvement of SARS-CoV-2 in a Polish Cohort of COVID-19-Positive Patients
- PMID: 33809199
- PMCID: PMC8001647
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18062916
Ocular Involvement of SARS-CoV-2 in a Polish Cohort of COVID-19-Positive Patients
Abstract
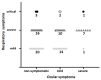
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 responsible for the current human COVID-19 pandemic has shown tropism toward different organs with variable efficiency, eyes included. The purpose of this study has been to investigate the presence of detectable SARS-CoV-2 infection in ocular swabs in patients affected by COVID-19. A consecutive series of 74 COVID-19-positive patients (age 21-89) were enrolled at two Polish COVID-19 hospitals for 4 months and were characterized by PCR for the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 genetic material in nasopharyngeal (NP) and ocular swabs, while their respiratory and ocular symptoms were noted. Almost 50% of them presented with severe/critical respiratory involvement, and some degree of eye disease. No tight correlation was observed between the presence of ocular and respiratory symptoms. Three male patients presenting with severe/critical lung disease tested positive in ocular swab, however with mild/moderate ocular symptoms. In conclusion, our study lends further support to the view that overt ocular infection by the SARS-CoV-2 virus is not such a frequent occurrence.
Keywords: COVID-19; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; eye; lung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tognetto D., Brézin A.P., Cummings A.B., Malyugin B.E., Kemer O.E., Prieto I., Rejdak R., Teus M.A., Törnblom R., Toro M.D., et al. Rethinking Elective Cataract Surgery Diagnostics, Assessments, and Tools after the COVID-19 Pandemic Experience and Beyond: Insights from the EUROCOVCAT Group. Diagnostics. 2020;10:1035. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10121035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

