Epigenetic Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Disease
- PMID: 33809263
- PMCID: PMC7998165
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061265
Epigenetic Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Disease
Abstract
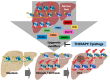
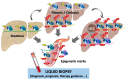
Research in the last decades has demonstrated the relevance of epigenetics in controlling gene expression to maintain cell homeostasis, and the important role played by epigenome alterations in disease development. Moreover, the reversibility of epigenetic marks can be harnessed as a therapeutic strategy, and epigenetic marks can be used as diagnosis biomarkers. Epigenetic alterations in DNA methylation, histone post-translational modifications (PTMs), and non-coding RNA (ncRNA) expression have been associated with the process of hepatocarcinogenesis. Here, we summarize epigenetic alterations involved in the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease (CLD), particularly focusing on DNA methylation. We also discuss their utility as epigenetic biomarkers in liquid biopsy for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Finally, we discuss the potential of epigenetic therapeutic strategies for HCC treatment.
Keywords: DNA methylation; epidrugs; hepatocellular carcinoma; liquid biopsy; liver fibrosis; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

