Incorporating Machine Learning into Established Bioinformatics Frameworks
- PMID: 33809353
- PMCID: PMC8000113
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22062903
Incorporating Machine Learning into Established Bioinformatics Frameworks
Abstract
The exponential growth of biomedical data in recent years has urged the application of numerous machine learning techniques to address emerging problems in biology and clinical research. By enabling the automatic feature extraction, selection, and generation of predictive models, these methods can be used to efficiently study complex biological systems. Machine learning techniques are frequently integrated with bioinformatic methods, as well as curated databases and biological networks, to enhance training and validation, identify the best interpretable features, and enable feature and model investigation. Here, we review recently developed methods that incorporate machine learning within the same framework with techniques from molecular evolution, protein structure analysis, systems biology, and disease genomics. We outline the challenges posed for machine learning, and, in particular, deep learning in biomedicine, and suggest unique opportunities for machine learning techniques integrated with established bioinformatics approaches to overcome some of these challenges.
Keywords: bioinformatics methods; deep learning; machine learning; phylogenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
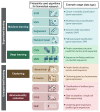

References
-
- Pevsner J. Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2015. Funtional Genomics.
-
- Ayyildiz D., Piazza S. Methods in Molecular Biology. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2019. Introduction to Bioinformatics. - PubMed
-
- Wodarz D., Komarova N. Computational Biology of Cancer. World Scientific; Singapore: 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

