Direct and Indirect Neurotoxic Potential of Metal/Metalloids in Plants and Fungi Used for Food, Dietary Supplements, and Herbal Medicine
- PMID: 33809439
- PMCID: PMC7998285
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics9030057
Direct and Indirect Neurotoxic Potential of Metal/Metalloids in Plants and Fungi Used for Food, Dietary Supplements, and Herbal Medicine
Abstract
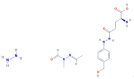
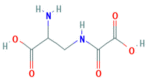
Plants and mushrooms bioconcentrate metals/metalloids from soil and water such that high levels of potentially neurotoxic elements can occur in cultivated and wild species used for food. While the health effects of excessive exposure to metals/metalloids with neurotoxic potential are well established, overt neurological disease from prolonged ingestion of contaminated botanicals has not been recognized. However, the presence of metal elements may affect levels of botanical neurotoxins in certain plants and mushrooms that are established causes of acute and chronic neurological disease.
Keywords: cassava; grasspea; heavy metals; morels; neurodegeneration; soil and water pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sposito G. The Chemistry of Soils. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: New York, NY, USA: 2008.
-
- Briggs E.D., Mobilization of Metals by Fungi in Historic Cemeteries . Bachelor’s Thesis. Bates College; Lewiston, MI, USA: 2015. [(accessed on 14 March 2021)]. Available online: https://scarab.bates.edu/geology_theses/25.
-
- Morley G.F., Sayer J.A., Wilkinson S.C., Ghareib M.M., Gadd G.M. Fungal sequestration, mobilization, and transformation of metals and metalloids. In: Frankland J.C., Magan N., Gadd G.M., editors. Fungi and Environmental Change. Cambridge University Press; New York, NY, USA: 1996. pp. 235–256.
-
- Colpaert J.V., Van Tichelen K.K. Mycorrhizas and environmental stress. In: Frankland J., Magan J., Gadd G.M., editors. Fungi and Environmental Change. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1996. British Mycological Society Symposia (20) - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

