Dielectric Properties of Ovine Heart at Microwave Frequencies
- PMID: 33809672
- PMCID: PMC8002248
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11030531
Dielectric Properties of Ovine Heart at Microwave Frequencies
Abstract
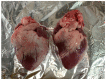
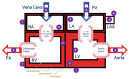
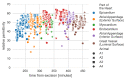
Accurate knowledge of the dielectric properties of biological tissues is important in dosimetry studies and for medical diagnostic, monitoring and therapeutic technologies. In particular, the dielectric properties of the heart are used in numerical simulations of radiofrequency and microwave heart ablation. In one recent study, it was demonstrated that the dielectric properties of different components of the heart can vary considerably, contrary to previous literature that treated the heart as a homogeneous organ with measurements that ignored the anatomical location. Therefore, in this study, we record and report the dielectric properties of the heart as a heterogeneous organ. We measured the dielectric properties at different locations inside and outside of the heart over the 500 MHz to 20 GHz frequency range. Different parts of the heart were identified based on the anatomy of the heart and their function; they include the epicardium, endocardium, myocardium, exterior and interior surfaces of atrial appendage, and the luminal surface of the great vessels. The measured dielectric properties for each part of the heart are reported at both a single frequency (2.4 GHz), which is of interest in microwave medical applications, and as parameters of a broadband Debye model. The results show that in terms of dielectric properties, different parts of the heart should not be considered the same, with more than 25% difference in dielectric properties between some parts. The specific Debye models and single frequency dielectric properties from this study can be used to develop more detailed models of the heart to be used in electromagnetic modeling.
Keywords: ablation; atrial fibrillation; biological tissues; dielectric properties; electromagnetic heating; heart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Klauenberg B.J., Miklavčič D., editors. Radio Frequency Radiation Dosimetry and Its Relationship to the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2000. - DOI
-
- Chiang J., Hynes K., Brace C.L. Flow-Dependent Vascular Heat Transfer during Microwave Thermal Ablation; Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; San Diego, CA, USA. 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5582–5585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pillai K., Akhter J., Chua T.C., Shehata M., Alzahrani N., Al-Alem I., Morris D.L. Heat Sink Effect on Tumor Ablation Characteristics as Observed in Monopolar Radiofrequency, Bipolar Radiofrequency, and Microwave, Using Ex Vivo Calf Liver Model. Medicine. 2015;94 doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

