Effect of NIR Laser Therapy by MLS-MiS Source on Fibroblast Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines in Relation to Wound Healing
- PMID: 33809724
- PMCID: PMC8002295
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9030307
Effect of NIR Laser Therapy by MLS-MiS Source on Fibroblast Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines in Relation to Wound Healing
Abstract
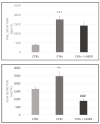
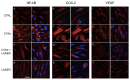
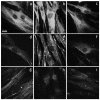
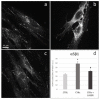
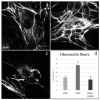
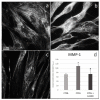
The fine control of inflammation following injury avoids fibrotic scars or impaired wounds. Due to side effects by anti-inflammatory drugs, the research is continuously active to define alternative therapies. Among them, physical countermeasures such as photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) are considered effective and safe. To study the cellular and molecular events associated with the anti-inflammatory activity of PBMT by a dual-wavelength NIR laser source, human dermal fibroblasts were exposed to a mix of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α) followed by laser treatment once a day for three days. Inducible inflammatory key enzymatic pathways, as iNOS and COX-2/mPGES-1/PGE2, were upregulated by the cytokine mix while PBMT reverted their levels and activities. The same behavior was observed with the proangiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), involved in neovascularization of granulation tissue. From a molecular point of view, PBMT retained NF-kB cytoplasmatic localization. According to a change in cell morphology, differences in expression and distribution of fundamental cytoskeletal proteins were observed following treatments. Tubulin, F-actin, and α-SMA changed their organization upon cytokine stimulation, while PBMT reestablished the basal localization. Cytoskeletal rearrangements occurring after inflammatory stimuli were correlated with reorganization of membrane α5β1 and fibronectin network as well as with their upregulation, while PBMT induced significant downregulation. Similar changes were observed for collagen I and the gelatinolytic enzyme MMP-1. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that the proposed NIR laser therapy is effective in controlling fibroblast activation induced by IL-1β and TNF-α, likely responsible for a deleterious effect of persistent inflammation.
Keywords: NIR laser radiation; fibroblasts; inflammation; photobiomodulation; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Photobiomodulation therapy action in wound repair skin induced in aged rats old: time course of biomarkers inflammatory and repair.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Nov;32(8):1769-1782. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2254-2. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28681084
-
Effects of photobiomodulation therapy, pharmacological therapy, and physical exercise as single and/or combined treatment on the inflammatory response induced by experimental osteoarthritis.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Jan;32(1):101-108. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-2091-8. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27726040
-
Effects of photobiomodulation therapy and topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug on skeletal muscle injury induced by contusion in rats-part 2: biochemical aspects.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Nov;32(8):1879-1887. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2299-2. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28795275
-
Effect of photobiomodulation therapy on inflammatory cytokines in healing dynamics of diabetic wounds: a systematic review of preclinical studies.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023 Jun;129(3):663-670. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2020.1861025. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 33370535
-
Wound Healing and Cell Dynamics Including Mesenchymal and Dental Pulp Stem Cells Induced by Photobiomodulation Therapy: An Example of Socket-Preserving Effects after Tooth Extraction in Rats and a Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 18;21(18):6850. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186850. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphenolic Profile and Biological Activities in HT29 Intestinal Epithelial Cells of Feijoa sellowiana Fruit Extract.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 14;26(16):7851. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167851. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869171 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation therapy in keloid management: a comprehensive review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;12:1550662. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1550662. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40703263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Microgravity on Endothelial Cell Function, Angiogenesis, and Vessel Remodeling During Wound Healing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Sep 22;9:720091. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.720091. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34631676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review via text mining approaches of human and veterinary applications of photobiomodulation: focus on multiwave locked system laser therapy.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Jul 18;40(1):321. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04572-y. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40679542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of fibroblasts in wound healing and tissue remodeling on Earth and in space.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 4;10:958381. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.958381. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36267456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

