Obesity and Energy Substrate Transporters in Ovarian Cancer-Review
- PMID: 33809784
- PMCID: PMC8002293
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26061659
Obesity and Energy Substrate Transporters in Ovarian Cancer-Review
Abstract
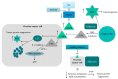
Ovarian cancer is the seventh most common cancer in women. It is characterized by a high mortality rate because of its aggressiveness and advanced stage at the time of diagnosis. It is a nonhomogenous group of neoplasms and, of which the molecular basics are still being investigated. Nowadays, the golden standard in the treatment is debulking cytoreductive surgery combined with platinum-based chemotherapy. We have presented the interactions and the resulting perspectives between fatty acid transporters, glucose transporters and ovarian cancer cells. Studies have shown the association between a lipid-rich environment and cancer progression, which suggests the use of correspondent transporter inhibitors as promising chemotherapeutic agents. This review summarizes preclinical and clinical studies highlighting the role of fatty acid transport proteins and glucose transporters in development, growth, metastasizing and its potential use in targeted therapies of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: cancer progression; lipids; obesity; ovarian cancer; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Torre L.A., Trabert B., DeSantis C.E., Miller K.D., Samimi G., Runowicz C.D., Gaudet M.M., Jemal A., Siegel R.L. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. [(accessed on 29 May 2018)];CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018 68:284–296. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29809280. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Konstantinopoulos P.A., Ceccaldi R., Shapiro G.I., D’Andrea A.D. Homologous Recombination Deficiency: Exploiting the Fundamental Vulnerability of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:1137–1154. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

