Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice
- PMID: 33809809
- PMCID: PMC8002527
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9030266
Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Combined with Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Intranasal Adjuvant Triggers Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Enhances Adaptive Immune Responses to an Inactivated PRRSV Vaccine in ICR Mice
Abstract
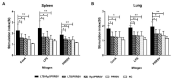
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is a major pathogen that has threatened the global swine industry for almost 30 years. Because current vaccines do not provide complete protection, exploration of new preventive strategies is urgently needed. Here, we combined a heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit of Escherichia coli (LTB) and ginsenoside Rg1 to form an intranasal adjuvant and evaluated its enhancement of immune responses in mice when added to an inactivated-PRRSV vaccine. The combination adjuvant synergistically elicited higher neutralizing and non-neutralizing (immunoglobulin G and A) antibody responses in the circulatory system and respiratory tract, and enhanced T and B lymphocyte proliferation, CD4+ T-cell priming, and cytotoxic CD4+ T cell activities in mononuclear cells from spleen and lung tissues when compared to the PRRSV vaccine alone, and it resulted in balanced Th1/Th2/Th17 responses. More importantly, we observed that the combination adjuvant also up-regulated type I interferon signaling, which may contribute to improvement in adaptive immune responses. These results highlight the potential value of a combined adjuvant approach for improving the efficacy of vaccination against PRRSV. Further study is required to evaluate the efficacy of this combined adjuvant in swine.
Keywords: LTB; PRRSV; Rg1; intranasal adjuvant; type I interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Linhares D.C., Cano J.P., Wetzell T., Nerem J., Torremorell M., Dee S.A. Effect of modified-live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSv) vaccine on the shedding of wild-type virus from an infected population of growing pigs. Vaccine. 2012;30:407–413. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.10.075. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

