Delivery Systems for Nucleic Acids and Proteins: Barriers, Cell Capture Pathways and Nanocarriers
- PMID: 33809969
- PMCID: PMC8004853
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030428
Delivery Systems for Nucleic Acids and Proteins: Barriers, Cell Capture Pathways and Nanocarriers
Abstract
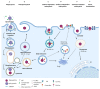
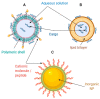
Gene therapy has been used as a potential approach to address the diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases and inherited disorders. In this line, non-viral systems have been exploited as promising alternatives for delivering therapeutic transgenes and proteins. In this review, we explored how biological barriers are effectively overcome by non-viral systems, usually nanoparticles, to reach an efficient delivery of cargoes. Furthermore, this review contributes to the understanding of several mechanisms of cellular internalization taken by nanoparticles. Because a critical factor for nanoparticles to do this relies on the ability to escape endosomes, researchers have dedicated much effort to address this issue using different nanocarriers. Here, we present an overview of the diversity of nanovehicles explored to reach an efficient and effective delivery of both nucleic acids and proteins. Finally, we introduced recent advances in the development of successful strategies to deliver cargoes.
Keywords: delivery; gene therapy; internalization; nanovehicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanocarriers address intracellular barriers for efficient drug delivery, overcoming drug resistance, subcellular targeting and controlled release.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Apr;207:115239. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115239. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38437916 Review.
-
Polymeric Nanocarriers for Non-Viral Gene Delivery.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015 May;11(5):739-70. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2015.2069. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26349389 Review.
-
Carriers Break Barriers in Drug Delivery: Endocytosis and Endosomal Escape of Gene Delivery Vectors.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Jul 16;52(7):1750-1760. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00177. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31243966 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarriers Conjugated with Cell Penetrating Peptides: New Trojan Horses by Modern Ulysses.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(8):700-22. doi: 10.2174/1389201017666160415155145. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27087493 Review.
-
Recent Advances and Challenges in Gene Delivery Mediated by Polyester-Based Nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug 31;16:5981-6002. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S321329. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34511901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Form Equals Function: Influence of Coacervate Architecture on Drug Delivery Applications.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Nov 11;10(11):6766-6789. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01105. Epub 2024 Oct 18. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 39423330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the Effect of Nucleic Acid Vaccines in the Treatment of HPV-Related Cancers: An Overview of Delivery Systems.Pathogens. 2022 Nov 30;11(12):1444. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11121444. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36558778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of the Composition of Cationic Liposomes on the Performance of Cargo Immunostimulatory RNA.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 23;15(9):2184. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092184. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765155 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of Various Cargos into Cancer Cells and Tissues via Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Review of the Last Decade.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 2;13(9):1391. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091391. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Innate Immunity by Therapeutic Nucleic Acids.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13360. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413360. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santos S.A., Vidigal P.M., Thrimawithana A., Betancourth B.M., Guimarães L.M., Templeton M.D., Alfenas A.C. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal different pathogenicity-related genes among three eucalyptus fungal pathogens. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2020;137:103332. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2019.103332. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagasaki T., Shinkai S. The concept of molecular machinery is useful for design of stimuli-responsive gene delivery systems in the mammalian cell. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007;58:205–219. doi: 10.1007/s10847-007-9303-6. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

