The Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activity of Greenly Synthesized Selenium and Zinc Composite Nanoparticles Using Ephedra aphylla Extract
- PMID: 33809976
- PMCID: PMC8005055
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11030470
The Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activity of Greenly Synthesized Selenium and Zinc Composite Nanoparticles Using Ephedra aphylla Extract
Abstract
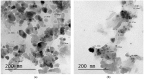
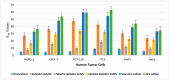
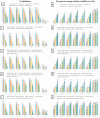
The current work aimed to synthesize selenium and zinc nanoparticles using the aqueous extract of Ephedra aphylla as a valuable medicinal plant. The prepared nanoparticles were characterized by TEM, zeta potential, and changes in the phytochemical constituents. Hence, the phenolic, flavonoid, and tannin contents were reduced in the case of the prepared samples of nanoparticles than the original values in the aqueous extract. The prepared extract of Ephedra aphylla and its selenium and zinc nanoparticles showed high potency as antioxidant agents as a result of the DPPH• assay. The samples were assessed as anticancer agents against six tumor cells and a normal lung fibroblast (WI-38) cell line. The selenium nanoparticles of Ephedra aphylla extract revealed very strong cytotoxicity against HePG-2 cells (inhibitory concentration (IC50) = 7.56 ± 0.6 µg/mL), HCT-116 cells (IC50 = 10.02 ± 0.9 µg/mL), and HeLa cells (IC50 = 9.23 ± 0.8 µg/mL). The samples were evaluated as antimicrobial agents against bacterial and fungal strains. Thus, selenium nanoparticles showed potent activities against Gram-negative strains (Salmonella typhimurium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli), Gram-positive strains (Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis), and the fungal strain Candida albicans. In conclusion, the preparation of nanoparticles of either selenium or zinc is crucial for improved biological characteristics.
Keywords: Ephedra aphylla; antimicrobial; antioxidant; aqueous extract; cancer; cytotoxic; nanoparticles; oxidation; selenium; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- El-Shahaby O.A., El-Zayat M., El-Fattah G.A., El-Hefny M.M. Evaluation of the biological activity of Capparis spinosa var. aegyptiaca essential oils and fatty constituents as Anticipated Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agents. Prog. Chem. Biochem. Res. 2019;2:211–221. doi: 10.33945/SAMI/PCBR.2019.4.6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

