Crystal Structure of a Phospholipase D from the Plant-Associated Bacteria Serratia plymuthica Strain AS9 Reveals a Unique Arrangement of Catalytic Pocket
- PMID: 33809980
- PMCID: PMC8004604
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22063219
Crystal Structure of a Phospholipase D from the Plant-Associated Bacteria Serratia plymuthica Strain AS9 Reveals a Unique Arrangement of Catalytic Pocket
Abstract
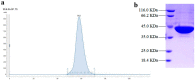
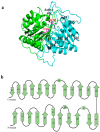
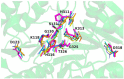
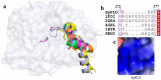
Phospholipases D (PLDs) play important roles in different organisms and in vitro phospholipid modifications, which attract strong interests for investigation. However, the lack of PLD structural information has seriously hampered both the understanding of their structure-function relationships and the structure-based bioengineering of this enzyme. Herein, we presented the crystal structure of a PLD from the plant-associated bacteria Serratia plymuthica strain AS9 (SpPLD) at a resolution of 1.79 Å. Two classical HxKxxxxD (HKD) motifs were found in SpPLD and have shown high structural consistence with several PLDs in the same family. While comparing the structure of SpPLD with the previous resolved PLDs from the same family, several unique conformations on the C-terminus of the HKD motif were demonstrated to participate in the arrangement of the catalytic pocket of SpPLD. In SpPLD, an extented loop conformation between β9 and α9 (aa228-246) was found. Moreover, electrostatic surface potential showed that this loop region in SpPLD was positively charged while the corresponding loops in the two Streptomyces originated PLDs (PDB ID: 1F0I, 2ZE4/2ZE9) were neutral. The shortened loop between α10 and α11 (aa272-275) made the SpPLD unable to form the gate-like structure which existed specically in the two Streptomyces originated PLDs (PDB ID: 1F0I, 2ZE4/2ZE9) and functioned to stabilize the substrates. In contrast, the shortened loop conformation at this corresponding segment was more alike to several nucleases (Nuc, Zuc, mZuc, NucT) within the same family. Moreover, the loop composition between β11 and β12 was also different from the two Streptomyces originated PLDs (PDB ID: 1F0I, 2ZE4/2ZE9), which formed the entrance of the catalytic pocket and were closely related to substrate recognition. So far, SpPLD was the only structurally characterized PLD enzyme from Serratia. The structural information derived here not only helps for the understanding of the biological function of this enzyme in plant protection, but also helps for the understanding of the rational design of the mutant, with potential application in phospholipid modification.
Keywords: Serratia plymuthica strain AS9; bioinformatics; crystal structure; phospholipase D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

