Indoor Air Quality in Buildings: A Comprehensive Review on the Factors Influencing Air Pollution in Residential and Commercial Structure
- PMID: 33810001
- PMCID: PMC8004912
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18063276
Indoor Air Quality in Buildings: A Comprehensive Review on the Factors Influencing Air Pollution in Residential and Commercial Structure
Abstract
Worldwide people tend to spend approximately 90% of their time in different indoor environments. Along with the penetration of outside air pollutants, contaminants are produced in indoor environments due to different activities such as heating, cooling, cooking, and emissions from building products and the materials used. As people spend most of their lives in indoor environments, this has a significant influence on human health and productivity. Despite the two decades of indoor air quality (IAQ) research from different perspectives, there is still a lack of comprehensive evaluation of peer-reviewed IAQ studies that specifically covers the relationship between the internal characteristics of different types of building environments with IAQ to help understand the progress and limitations of IAQ research worldwide. Therefore, this review of scientific studies presents a broad spectrum of pollutants identified in both residential and commercial indoor environments, highlighting the trends and gaps in IAQ research. Moreover, analysis of literature data enabled us to assess the different IAQs in buildings located in different countries/regions, thus reflecting the current global scientific understanding of IAQ. This review has the potential to benefit building professionals by establishing indoor air regulations that account for all indoor contaminant sources to create healthy and sustainable building environments.
Keywords: indoor air pollution; influencing factors indoor; office indoor pollutants; residential indoor pollutants; school indoor pollutants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

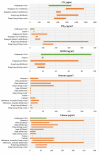
Similar articles
-
Indoor air quality in green buildings: A case-study in a residential high-rise building in the northeastern United States.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2015;50(3):225-42. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2015.981101. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2015. PMID: 25594117
-
A review of critical residential buildings parameters and activities when investigating indoor air quality and pollutants.Indoor Air. 2022 Nov;32(11):e13144. doi: 10.1111/ina.13144. Indoor Air. 2022. PMID: 36437669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seasonal variation in indoor concentrations of air pollutants in residential buildings.J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2021 Jun;71(6):761-777. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2021.1895367. Epub 2021 Mar 22. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33625321
-
A review of relevant parameters for assessing indoor air quality in educational facilities.Environ Res. 2024 Nov 15;261:119713. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119713. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 39094896 Review.
-
A seasonal investigation of indoor air quality in relation to architectural features in government office buildings in Enugu, Nigeria.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 6;14(1):26885. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78160-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39506068 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hospital indoor air quality and its relationships with building design, building operation, and occupant-related factors: A mini-review.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 8;10:1067764. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1067764. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36424957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoor Pollen Concentrations of Mountain Cedar (Juniperus ashei) during Rainy Episodes in Austin, Texas.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 29;19(3):1541. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031541. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162567 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosustainability.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Aug 29;18:1436179. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1436179. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39268220 Free PMC article.
-
Field measurement study of indoor thermal environment of badminton halls in a hot summer and cold winter region in different seasons in China.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 18;10(15):e34883. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34883. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39144935 Free PMC article.
-
Public Health Relevance of US EPA Air Quality Index Activity Recommendations.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Apr 1;7(4):e245292. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5292. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38587845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klepeis N.E., Nelson W.C., Ott W.R., Robinson J.P., Tsang A.M., Switzer P., Behar J.V., Hern S.C., Engelmann W.H. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001;11:231–252. doi: 10.1038/sj.jea.7500165. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EPA Indoor Air Pollution and Health. Report Series No. 104. [(accessed on 23 March 2020)];2013 Available online: https://www.epa.ie/pubs/reports/research/health/IndoorAirPollutionandHea....
-
- Sisask M., Värnik P., Värnik A., Apter A., Balazs J., Balint M., Bobes J., Brunner R., Corcoran P., Cosman D., et al. Teacher satisfaction with school and psychological well-being affects their readiness to help children with mental health problems. Health Educ. J. 2014;73:382–393. doi: 10.1177/0017896913485742. - DOI
-
- Jones A.P. Indoor air quality and health. Atmos. Environ. 1999;33:4535–4564. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00272-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

