Mammalian and Avian Host Cell Influenza A Restriction Factors
- PMID: 33810083
- PMCID: PMC8005160
- DOI: 10.3390/v13030522
Mammalian and Avian Host Cell Influenza A Restriction Factors
Abstract
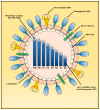
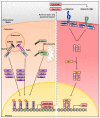
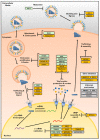
The threat of a new influenza pandemic is real. With past pandemics claiming millions of lives, finding new ways to combat this virus is essential. Host cells have developed a multi-modular system to detect incoming pathogens, a phenomenon called sensing. The signaling cascade triggered by sensing subsequently induces protection for themselves and their surrounding neighbors, termed interferon (IFN) response. This response induces the upregulation of hundreds of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), including antiviral effectors, establishing an antiviral state. As well as the antiviral proteins induced through the IFN system, cells also possess a so-called intrinsic immunity, constituted of antiviral proteins that are constitutively expressed, creating a first barrier preceding the induction of the interferon system. All these combined antiviral effectors inhibit the virus at various stages of the viral lifecycle, using a wide array of mechanisms. Here, we provide a review of mammalian and avian influenza A restriction factors, detailing their mechanism of action and in vivo relevance, when known. Understanding their mode of action might help pave the way for the development of new influenza treatments, which are absolutely required if we want to be prepared to face a new pandemic.
Keywords: influenza virus; innate immunity; interferon; restriction factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

