Virtual Reality Customized 360-Degree Experiences for Stress Relief
- PMID: 33810135
- PMCID: PMC8004715
- DOI: 10.3390/s21062219
Virtual Reality Customized 360-Degree Experiences for Stress Relief
Abstract
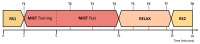
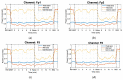
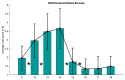
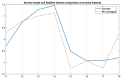
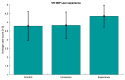
The latest studies in virtual reality (VR) have evidenced the potential of this technology to reproduce environments from multiple domains in an immersive way. For instance, in stress relief research, VR has been presented as a portable and inexpensive alternative to chromotherapy rooms, which require an adapted space and are expensive. In this work, we propose a portable and versatile alternative to the traditional chromotherapy color-loop treatment through four different 360-degree virtual experiences. A group of 23 healthy participants (mean age 22.65 ± 5.48) were conducted through a single-session experience divided into four phases while their electroencephalography (EEG) was recorded. First, they were stressed via the Montreal imaging stress task (MIST), and then relaxed using our VR proposal. We applied the Wilcoxon test to evaluate the relaxation effect in terms of the EEG relative gamma and self-perceived stress surveys. The results that we obtained validate the effectiveness of our 360-degree proposal to significantly reduce stress (p-value = 0.0001). Furthermore, the participants deemed our proposal comfortable and immersive (score above 3.5 out of 5). These results suggest that 360-degree VR experiences can mitigate stress, reduce costs, and bring stress relief assistance closer to the general public, like in workplaces or homes.
Keywords: EEG; emotions; stress; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Quantitative Assessment of Stress Through EEG During a Virtual Reality Stress-Relax Session.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 Jul 14;15:684423. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2021.684423. eCollection 2021. Front Comput Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34335216 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Reality as a Portable Alternative to Chromotherapy Rooms for Stress Relief: A Preliminary Study.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 30;20(21):6211. doi: 10.3390/s20216211. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33143361 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding subjective emotional arousal from EEG during an immersive virtual reality experience.Elife. 2021 Oct 28;10:e64812. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64812. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34708689 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Applications Using Immersive Virtual Reality: A Review on EEG Studies.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2023;31:1645-1658. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3254551. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2023. PMID: 37028309 Review.
-
Resilience-Building for Mental Health among Early Childhood Educators: A Systematic Review and Pilot-Study towards an EEG-VR Resilience Building Intervention.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 6;19(7):4413. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19074413. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35410097 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The neural correlates of psychosocial stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of spectral analysis EEG studies.Neurobiol Stress. 2022 Apr 26;18:100452. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100452. eCollection 2022 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2022. PMID: 35573807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Well-Being: A Comparative Study of Virtual Reality Chromotherapy Rooms with Static, Dynamic, and Empty Environments.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;24(6):1732. doi: 10.3390/s24061732. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543995 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Reality and Stress Management: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 15;16(7):e64573. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64573. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39144853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Stress Through EEG During a Virtual Reality Stress-Relax Session.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 Jul 14;15:684423. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2021.684423. eCollection 2021. Front Comput Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34335216 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences and perceptions of palliative care patients receiving virtual reality therapy: a meta-synthesis of qualitative studies.BMC Palliat Care. 2024 Jul 23;23(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12904-024-01520-5. BMC Palliat Care. 2024. PMID: 39044242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carl E., Stein A.T., Levihn-Coon A., Pogue J.R., Rothbaum B., Emmelkamp P., Asmundson G.J.G., Carlbring P., Powers M.B. Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy for Anxiety and Related Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Anxiety Disord. 2019;61:27–36. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ip H.H.S., Wong S.W.L., Chan D.F.Y., Byrne J., Li C., Yuan V.S.N., Lau K.S.Y., Wong J.Y.W. Enhance Emotional and Social Adaptation Skills for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Virtual Reality Enabled Approach. Comput. Educ. 2018;117:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2017.09.010. - DOI
-
- Maskey M., McConachie H., Rodgers J., Grahame V., Maxwell J., Tavernor L., Parr J.R. An Intervention for Fears and Phobias in Young People with Autism Spectrum Disorders Using Flat Screen Computer-Delivered Virtual Reality and Cognitive Behaviour Therapy. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2019;59:58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2018.11.005. - DOI
-
- Maggio M.G., Russo M., Cuzzola M.F., Destro M., La Rosa G., Molonia F., Bramanti P., Lombardo G., De Luca R., Calabrò R.S. Virtual Reality in Multiple Sclerosis Rehabilitation: A Review on Cognitive and Motor Outcomes. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019;65:106–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.03.017. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

