Immunoreactivity of Muscarinic Acetylcholine M2 and Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptors, Norepinephrine Transporter and Kir Channels in a Model of Epilepsy
- PMID: 33810231
- PMCID: PMC8066555
- DOI: 10.3390/life11040276
Immunoreactivity of Muscarinic Acetylcholine M2 and Serotonin 5-HT2B Receptors, Norepinephrine Transporter and Kir Channels in a Model of Epilepsy
Abstract
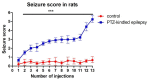
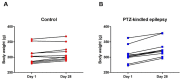
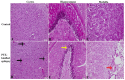
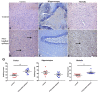
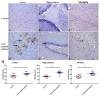
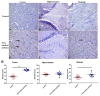
Epilepsy is characterized by an imbalance in neurotransmitter activity; an increased excitatory to an inhibitory activity. Acetylcholine (ACh), serotonin, and norepinephrine (NE) may modulate neural activity via several mechanisms, mainly through its receptors/transporter activity and alterations in the extracellular potassium (K+) concentration via K+ ion channels. Seizures may disrupt the regulation of inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) channels and alter the receptor/transporter activity. However, there are limited data present on the immunoreactivity pattern of these neurotransmitter receptors/transporters and K+ channels in chronic models of epilepsy, which therefore was the aim of this study. Changes in the immunoreactivity of epileptogenesis-related neurotransmitter receptors/transporters (M2, 5-HT2B, and NE transporter) as well as Kir channels (Kir3.1 and Kir6.2) were determined in the cortex, hippocampus and medulla of adult Wistar rats by utilizing a Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-kindling chronic epilepsy model. Increased immunoreactivity of the NE transporter, M2, and 5-HT2B receptors was witnessed in the cortex and medulla. While the immunoreactivity of the 5-HT2B receptor was found increased in the cortex and medulla, it was decreased in the hippocampus, with no changes observed in the M2 receptor in this region. Kir3.1 and Kir6.2 staining showed increase immunoreactivity in the cerebral cortex, but channel contrasting findings in the hippocampus and medulla. Our results suggest that seizure kindling may result in significant changes in the neurotransmitter system which may contribute or propagate to future epileptogenesis, brain damage and potentially towards sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). Further studies on the pathogenic role of these changes in neurotransmitter receptors/transporters and K+ channel immunoreactivity may identify newer possible targets to treat seizures or prevent epilepsy-related comorbidities.
Keywords: 5-HT2B; M2; PTZ; chronic epilepsy; norepinephrine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased ACh-Associated Immunoreactivity in Autonomic Centers in PTZ Kindling Model of Epilepsy.Biomedicines. 2020 May 8;8(5):113. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8050113. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32397136 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of cardiac inwardly rectifying potassium channels in pentylenetetrazole kindling model of epilepsy in rats.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018 Dec 31;64(15):47-54. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018. PMID: 30672436
-
Neuronal Kir3.1/Kir3.2a channels coupled to serotonin 1A and muscarinic m2 receptors are differentially modulated by the "short" RGS3 isoform.Neuropharmacology. 2005 Sep;49(4):465-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.04.010. Neuropharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15935408
-
Inwardly rectifying potassium channels: their molecular heterogeneity and function.Jpn J Physiol. 1997 Feb;47(1):11-39. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.47.11. Jpn J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9159640 Review.
-
Envisioning the role of inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channel in epilepsy.J Neurosci Res. 2022 Feb;100(2):413-443. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24985. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 34713909 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Response to Mismatch Novelty in the Li2+-Pilocarpine Rat Model of TLE: Correlation with Hippocampal Monoaminergic Inputs.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 12;12(3):631. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030631. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540244 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic receptor system as a pharmacological target in the treatment of epilepsy (Review).Med Int (Lond). 2024 Feb 27;4(2):20. doi: 10.3892/mi.2024.144. eCollection 2024 Mar-Apr. Med Int (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38476984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin receptors in epilepsy: Novel treatment targets?Epilepsia Open. 2022 Jun;7(2):231-246. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12580. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Epilepsia Open. 2022. PMID: 35075810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

