Kaempferia parviflora Rhizome Extract Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Toxicity in HT-22 Mouse Hippocampal Neuronal Cells and Extends Longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 33810282
- PMCID: PMC8066628
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10040264
Kaempferia parviflora Rhizome Extract Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Toxicity in HT-22 Mouse Hippocampal Neuronal Cells and Extends Longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
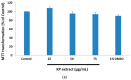
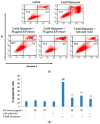
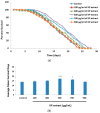
Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker (KP) or "Kra-chai-dam" has been shown to exhibit several pharmacological effects including anti-inflammation, antimicrobial, and sexual-enhancing activity. The objectives of this study included an investigation of the effect of KP rhizome extract against glutamate-induced toxicity in mouse hippocampal HT-22 neuronal cells, determination of the underlying mechanism of neuroprotection, and an evaluation of the effect of KP extract on the longevity of Caenorhabditis elegans. HT-22 cells were co-treated with glutamate (5 mM) and KP extract (25, 50, and 75 μg/mL) for 14 h. Cell viability, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) assay, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis, and Western blotting were performed. The longevity effect of KP extract on C. elegans was studied by lifespan measurement. In HT-22 cells, co-treatment of glutamate with KP extract significantly inhibited glutamate-mediated cytotoxicity and decreased intracellular ROS production. Additionally, the glutamate-induced apoptosis and apoptotic-inducing factor (AIF) translocation were blocked by KP extract co-treatment. Western blot analysis also demonstrated that KP extract significantly diminished extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation induced by glutamate, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was recovered to the control. Moreover, this KP extract treatment prolonged the lifespan of C. elegans. Altogether, this study suggested that KP extract possesses both neuroprotective and longevity-inducing properties, thus serving as a promising candidate for development of innovative health products.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; HT-22 mouse hippocampal neuronal cells; Kaempferia parviflora rhizome extract; glutamate toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization Thailand: Alzheimers/Dementia 2017. [(accessed on 10 July 2020)];2017 Available online: https://www.worldlifeexpectancy.com/thailand-alzheimers-dementia.
-
- Joseph T.C., Pamela P. Oxidative Stress, Glutamate, and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Science. 1993;262:689–695. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

