Expression of Musashi-1 Increases in Bone Healing
- PMID: 33810326
- PMCID: PMC8037090
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073395
Expression of Musashi-1 Increases in Bone Healing
Abstract
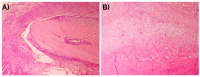
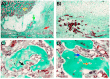
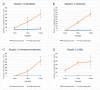
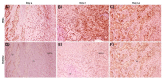
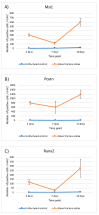
Musashi-1 (MSI1) is an RNA-binding protein that regulates progenitor cells in adult and developing organisms to maintain self-renewal capacities. The role of musashi-1 in the bone healing environment and its relation with other osteogenic factors is unknown. In the current study, we analyze the expression of MSI1 in an experimental model of rat femoral bone fractures. We also analyze the relation between MSI1 expression and the expression of two osteogenic markers: periostin (POSTN) and runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2). We use histological, immunohistochemical, and qPCR techniques to evaluate bone healing and the expression of MSI1, POSTN, and RUNX2 over time (4, 7, and 14 days). We compare our findings with non-fractured controls. We find that in bone calluses, the number of cells expressing MSI1 and RUNX2 increase over time and the intensity of POSTN expression decreases over time. Within bone calluses, we find the presence of MSI1 expression in mesenchymal stromal cells, osteoblasts, and osteocytes but not in hypertrophic chondrocytes. After 14 days, the expression of MSI1, POSTN, and RUNX2 was significantly correlated. Thus, we conclude that musashi-1 potentially serves in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells and bone healing. Therefore, further studies are needed to determine the possibility of musashi-1's role as a clinical biomarker of bone healing and therapeutic agent for bone regeneration.
Keywords: Musashi-1; Runx2; bone healing; mesenchymal stem cells; periostin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Expression of Musashi-1 During Osteogenic Differentiation of Oral MSC: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 2;20(9):2171. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092171. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052494 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects RUNX2 immunopositive osteogenic cells in delayed clinical fracture healing.Bone. 2009 Nov;45(5):862-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.07.012. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19631773
-
Increased Expression of Musashi-1 Evidences Mesenchymal Repair in Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 16;8(1):12243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29908-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30116022 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2.Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):189-95. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0832-8. Epub 2009 Aug 1. Cell Tissue Res. 2010. PMID: 19649655 Review.
-
Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in fracture healing.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998 Oct;(355 Suppl):S116-23. doi: 10.1097/00003086-199810001-00013. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. PMID: 9917632 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in the Research on RNA-Binding Proteins in Bone Development and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;25(14):7735. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147735. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation comparing bovine versus porcine bone xenografts mixed with autogenous bone graft. A split-mouth randomized controlled trial.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022 May;33(5):524-536. doi: 10.1111/clr.13912. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022. PMID: 35224778 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of RNA-binding proteins on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Feb;479(2):383-392. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04742-y. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37072640
-
MSI1 Stabilizes MACF1 to Inhibit Apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 Cells Induced by High Glucose and Promote Osteogenic Differentiation Through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;65(7):1085-1095. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00617-7. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36443618
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

