Effect of Varying Working Distances between Sandblasting Device and Composite Substrate Surface on the Repair Bond Strength
- PMID: 33810415
- PMCID: PMC8037222
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14071621
Effect of Varying Working Distances between Sandblasting Device and Composite Substrate Surface on the Repair Bond Strength
Abstract
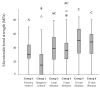
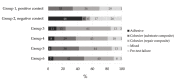
This study investigates the effect of defined working distances between the tip of a sandblasting device and a resin composite surface on the composite-composite repair bond strength. Resin composite specimens (Ceram.x Spectra ST (HV); Dentsply Sirona, Konstanz, Germany) were aged by thermal cycling (5000 cycles, 5-55 °C) and one week of water storage. Mechanical surface conditioning of the substrate surfaces was performed by sandblasting with aluminum oxide particles (50 µm, 3 bar, 10 s) from varying working distances of 1, 5, 10, and 15 mm. Specimens were then silanized and restored by application of an adhesive system and repair composite material (Ceram.x Spectra ST (HV)). In the negative control group, no mechanical surface pretreatment or silanization was performed. Directly applied inherent increments served as the positive control group (n = 8). After thermal cycling of all groups, microtensile repair bond strength was assessed, and surfaces were additionally characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The negative control group reached the significantly lowest microtensile bond strength of all groups. No significant differences in repair bond strength were observed within the groups with varying sandblasting distances. Composite surfaces sandblasted from a distance of 1 mm or 5 mm showed no difference in repair bond strength compared to the positive control group, whereas distances of 10 or 15 mm revealed significantly higher repair bond strengths than the inherent incremental bond strength (positive control group). In conclusion, all sandblasted test groups achieved similar or higher repair bond strength than the inherent incremental bond strength, indicating that irrespective of the employed working distance between the sandblasting device and the composite substrate surface, repair restorations can be successfully performed.
Keywords: aluminum oxide sandblasting; composite repair; microtensile bond strength; working distance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Composite Age on the Repair Bond Strength after Different Mechanical Surface Pretreatments.J Adhes Dent. 2020;22(4):365-372. doi: 10.3290/j.jad.a44867. J Adhes Dent. 2020. PMID: 32666062
-
Effect of Different Working Settings of Sandblasting on Resin Composite Repair Bond Strength.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;18(2):313. doi: 10.3390/ma18020313. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39859784 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of surface treatments on microtensile bond strength of repaired aged silorane resin composite.Oper Dent. 2013 Jan-Feb;38(1):91-9. doi: 10.2341/11-057-L. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Oper Dent. 2013. PMID: 22830537 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of different surface treatments and adhesives on repair bond strength of resin composites after one and 12 months of storage using an improved microtensile test method.Oper Dent. 2014 Sep-Oct;39(5):E206-16. doi: 10.2341/12-429-L. Epub 2014 May 7. Oper Dent. 2014. PMID: 24807815
-
[Application of different surface treatment methods in teeth restoration with nano composite resin].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2020 Dec;29(6):591-595. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33778824 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Surface Treatments on Repair Bond Strength of Aged Resin Composites.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022 Aug 29;12(4):449-455. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_99_22. eCollection 2022 Jul-Aug. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022. PMID: 36312574 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Repair Bond Strength of Dental Resin Composite after Sodium Bicarbonate or Aluminum Oxide Air-Abrasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 17;24(14):11568. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411568. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511327 Free PMC article.
-
Semidirect Resin Composite Veneers in a Patient with Bruxism.Case Rep Dent. 2024 Mar 22;2024:5572481. doi: 10.1155/2024/5572481. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Dent. 2024. PMID: 38560367 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Long-Term Repair Bond Strength of Aged Methacrylate-Based Resin Composite Restorations: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 5;2022:7708643. doi: 10.1155/2022/7708643. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 37964860 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sandblasting distances on the shear bond strength of a self-etch and total-etch adhesive system to cervical dentin in the gingival wall of Class II restorations.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025 Jul 24;22:30. doi: 10.4103/drj.drj_398_24. eCollection 2025. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025. PMID: 40786500 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

