Mechanisms of Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer: Adaptive Responses, Drug Tolerance and Cellular Plasticity
- PMID: 33810522
- PMCID: PMC8037590
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071538
Mechanisms of Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer: Adaptive Responses, Drug Tolerance and Cellular Plasticity
Abstract
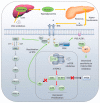
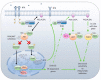
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway plays a central role in the regulation of several signalling cascades which regulate biological processes such as cellular growth, survival, proliferation, motility and angiogenesis. The hyperactivation of this pathway is linked to tumour progression and is one of the most common events in human cancers. Additionally, aberrant activation of the PI3K pathway has been demonstrated to limit the effectiveness of a number of anti-tumour agents paving the way for the development and implementation of PI3K inhibitors in the clinic. However, the overall effectiveness of these compounds has been greatly limited by inadequate target engagement due to reactivation of the pathway by compensatory mechanisms. Herein, we review the common adaptive responses that lead to reactivation of the PI3K pathway, therapy resistance and potential strategies to overcome these mechanisms of resistance. Furthermore, we highlight the potential role in changes in cellular plasticity and PI3K inhibitor resistance.
Keywords: PI3K pathway; PI3K pathway inhibitors; mechanisms of resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

