One-year myopia control efficacy of spectacle lenses with aspherical lenslets
- PMID: 33811039
- PMCID: PMC9340037
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-318367
One-year myopia control efficacy of spectacle lenses with aspherical lenslets
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the 1-year efficacy of two new myopia control spectacle lenses with lenslets of different asphericity.
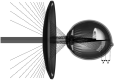
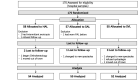
Methods: One hundred seventy schoolchildren aged 8-13 years with myopia of -0.75 D to -4.75 D were randomised to receive spectacle lenses with highly aspherical lenslets (HAL), spectacle lenses with slightly aspherical lenslets (SAL), or single-vision spectacle lenses (SVL). Cycloplegic autorefraction (spherical equivalent refraction (SER)), axial length (AL) and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were measured at baseline and 6-month intervals. Adaptation and compliance questionnaires were administered during all visits.
Results: After 1 year, the mean changes in the SER (±SE) and AL (±SE) in the SVL group were -0.81±0.06 D and 0.36±0.02 mm. Compared with SVL, the myopia control efficacy measured using SER was 67% (difference of 0.53 D) for HAL and 41% (difference of 0.33 D) for SAL, and the efficacy measured using AL was 64% (difference of 0.23 mm) for HAL and 31% (difference of 0.11 mm) for SAL (all p<0.01). HAL resulted in significantly greater myopia control than SAL for SER (difference of 0.21 D, p<0.001) and AL (difference of 0.12 mm, p<0.001). The mean BCVA (-0.01±0.1 logMAR, p=0.22) and mean daily wearing time (13.2±2.6 hours, p=0.26) were similar among the three groups. All groups adapted to their lenses with no reported adverse events, complaints or discomfort.
Conclusions: Spectacle lenses with aspherical lenslets effectively slow myopia progression and axial elongation compared with SVL. Myopia control efficacy increased with lenslet asphericity.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR1800017683.
Keywords: child health (paediatrics); clinical trial; optics and refraction; vision.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Jinhua Bao is an Associate Director of Wenzhou Medical University–Essilor International Research Centre. Adeline Yang, Ee Woon Lim, Daniel P. Spiegel and Björn Drobe are employees of Essilor International. This company supplied the study devices and holds the following patent applications related to this work: WO2019166653, WO2019166654, and WO2019166655. No conflicts of interest exist for the remaining authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
