How does COVID-19 impact psoriasis practice, prescription patterns, and healthcare delivery for psoriasis patients? A cross-sectional survey study
- PMID: 33811728
- PMCID: PMC8250824
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.14104
How does COVID-19 impact psoriasis practice, prescription patterns, and healthcare delivery for psoriasis patients? A cross-sectional survey study
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that needs continuous medical care. During COVID-19, delivering medical service was negatively affected.
Aims: To describe the impact of COVID-19 on psoriasis healthcare delivery, management, and practice.
Methods: This observational cross-sectional study was conducted on 197 dermatologists using a validated online questionnaire. The survey evaluated the effect of COVID-19 on the decisions, prescription patterns, appointments rescheduling, and healthcare delivery for psoriasis patients by dermatologists. The questionnaire was developed and validated with a reliability score >0.7.
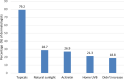
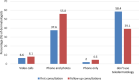
Results: During the pandemic, most dermatologists delayed initiating biological/immunosuppressive therapy for psoriasis unless urgently needed by the patient. For patients already receiving biologics or immunosuppressive treatment, most dermatologists favored continuation of therapy. Almost half (44.2%) of participants do not perform SARS-CoV-2 PCR screening before initiating biologics/immunosuppressive therapy. Dermatologists also reported an increased prescription of topical medications (79.2%), natural sunlight (28.4%), acitretin (26.9%), and home UVB (21.3%). Opinions regarding the use of hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment/prophylaxis for psoriasis patients were controversial. Intervals between face-to-face follow-up visits were prolonged by 71.6% of dermatologists. More than half of participants reported that their patients discontinued treatment without medical consultation. More than three fourth of responders either agreed or strongly agreed that COVID-19 negatively affected psoriasis patients.
Conclusions: The COVID-19 pandemic has a negative impact on psoriasis management and healthcare delivery. Dermatologists are cautious about using biologics and immunosuppressive drugs during the pandemic, making case-by-case decisions. Psoriasis patients need compliance monitoring, and psychological support during the pandemic, which can be facilitated by teledermatology.
Keywords: PCR; SARS-CoV-2; biologics; coronavirus; immunosuppressive; psoriasis.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Timeline: WHO's COVID‐19 response. Available from. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/interact.... Accessed December 22, 2020.
-
- Worldometer . COVID‐19 Coronavirus pandemic Update. 2020. Available from https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/Accessed December 22, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

