Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-Cov-2
- PMID: 33811811
- PMCID: PMC7985926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959
Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-Cov-2
Abstract
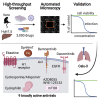
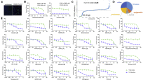
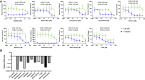
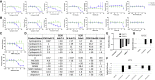
There is an urgent need for antivirals to treat the newly emerged severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). To identify new candidates, we screen a repurposing library of ∼3,000 drugs. Screening in Vero cells finds few antivirals, while screening in human Huh7.5 cells validates 23 diverse antiviral drugs. Extending our studies to lung epithelial cells, we find that there are major differences in drug sensitivity and entry pathways used by SARS-CoV-2 in these cells. Entry in lung epithelial Calu-3 cells is pH independent and requires TMPRSS2, while entry in Vero and Huh7.5 cells requires low pH and triggering by acid-dependent endosomal proteases. Moreover, we find nine drugs are antiviral in respiratory cells, seven of which have been used in humans, and three are US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved, including cyclosporine. We find that the antiviral activity of cyclosporine is targeting Cyclophilin rather than calcineurin, revealing essential host targets that have the potential for rapid clinical implementation.
Keywords: HTS; SARS2; TMPRSS2; antiviral; coronavirus; cyclophilin; cyclosporin; drugs; entry; screening.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ashburn T.T., Thor K.B. Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:673–683. - PubMed
-
- Beigel J.H., Tomashek K.M., Dodd L.E., Mehta A.K., Zingman B.S., Kalil A.C., Hohmann E., Chu H.Y., Luetkemeyer A., Kline S., et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 - Preliminary Report. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

