Reactive astrocytes: The nexus of pathological and clinical hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 33812051
- PMCID: PMC8168445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101335
Reactive astrocytes: The nexus of pathological and clinical hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
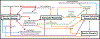
Astrocyte reactivity is a hallmark of neuroinflammation that arises with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and nearly every other neurodegenerative condition. While astrocytes certainly contribute to classic inflammatory processes (e.g. cytokine release, waste clearance, and tissue repair), newly emerging technologies for measuring and targeting cell specific activities in the brain have uncovered essential roles for astrocytes in synapse function, brain metabolism, neurovascular coupling, and sleep/wake patterns. In this review, we use a holistic approach to incorporate, and expand upon, classic neuroinflammatory concepts to consider how astrocyte dysfunction/reactivity modulates multiple pathological and clinical hallmarks of AD. Our ever-evolving understanding of astrocyte signaling in neurodegeneration is not only revealing new drug targets and treatments for dementia but is suggesting we reimagine AD pathophysiological mechanisms.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Astrocytes; Dementia; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Reactive astrocytes.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Allweis C, Landau T, Abeles M, Magnes J, 1966. The oxidation of uniformly labelled albumin-bound palmitic acid to CO2 by the perfused cat brain. J. Neurochem 13 (9), 795–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

