Prone positioning in intubated and mechanically ventilated patients with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33812212
- PMCID: PMC8006210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2021.110258
Prone positioning in intubated and mechanically ventilated patients with SARS-CoV-2
Figures
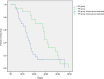
Comment on
-
Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.N Engl J Med. 2013 Jun 6;368(23):2159-68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214103. Epub 2013 May 20. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23688302 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cummings M.J., Baldwin M.R., Abrams D., Jacobson S.D., Meyer B.J., Balough E.M., et al. Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10239):1763–1770. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31189-2. Epub 2020/05/23. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., Shu H., Xia J., Liu H., et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475–481. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30079-5. Epub 2020/02/28. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piroth L., Cottenet J., Mariet A.S., Bonniaud P., Blot M., Tubert-Bitter P., et al. Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: a nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30527-0. Epub 2020/12/21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krishnan S., Patel K., Desai R., Sule A., Paik P., Miller A., et al. Clinical comorbidities, characteristics, and outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients in the State of Michigan with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. J Clin Anesth. 2020;67:110005. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2020.110005. Epub 2020/07/25. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

