Intrinsically disordered proteins and biomolecular condensates as drug targets
- PMID: 33812316
- PMCID: PMC7616887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.02.009
Intrinsically disordered proteins and biomolecular condensates as drug targets
Abstract
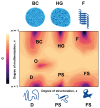
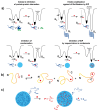
Intrinsically disordered domains represent attractive therapeutic targets because they play key roles in cancer, as well as in neurodegenerative and infectious diseases. They are, however, considered undruggable because they do not form stable binding pockets for small molecules and, therefore, have not been prioritized in drug discovery. Under physiological solution conditions many biomedically relevant intrinsically disordered proteins undergo phase separation processes leading to the formation of mesoscopic highly dynamic assemblies, generally known as biomolecular condensates that define environments that can be quite different from the solutions surrounding them. In what follows, we review key recent findings in this area and show how biomolecular condensation can offer opportunities for modulating the activities of intrinsically disordered targets.
Keywords: Biomolecular condensates; Drug discovery; Free energy landscape; Intrinsically disordered proteins.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest M.F-V. is an employee of Dewpoint Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Heller GT, Bonomi M, Vendruscolo M. Structural Ensemble Modulation upon Small-Molecule Binding to Disordered Proteins. J Mol Biol. 2018;430:2288–2292. - PubMed
-
- Hyman AA, Weber CA, Jülicher F. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:39–58. [*The authors provide a clear and comprehensive review of how liquid-liquid phase separation leads to the formation of cellular assemblies with key biological functions.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

