Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure in Diabetes
- PMID: 33813813
- PMCID: PMC8024162
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0282
Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure in Diabetes
Erratum in
-
Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure in Diabetes.Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Sep;45(5):796. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0239. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 34610726 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
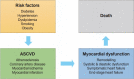
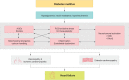
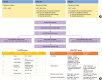
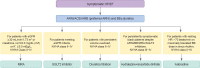
The cardiovascular disease continuum begins with risk factors such as diabetes mellitus (DM), progresses to vasculopathy and myocardial dysfunction, and finally ends with cardiovascular death. Diabetes is associated with a 2- to 4-fold increased risk for heart failure (HF). Moreover, HF patients with DM have a worse prognosis than those without DM. Diabetes can cause myocardial ischemia via micro- and macrovasculopathy and can directly exert deleterious effects on the myocardium. Hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance can cause alterations in vascular homeostasis. Then, reduced nitric oxide and increased reactive oxygen species levels favor inflammation leading to atherothrombotic progression and myocardial dysfunction. The classification, diagnosis, and treatment of HF for a patient with and without DM remain the same. Until now, drugs targeting neurohumoral and metabolic pathways improved mortality and morbidity in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Therefore, all HFrEF patients should receive guideline-directed medical therapy. By contrast, drugs modulating neurohumoral activity did not improve survival in HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) patients. Trials investigating whether sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors are effective in HFpEF are on-going. This review will summarize the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment of HF in diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic cardiomyopathies; Diagnosis; Epidemiology; Heart failure; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Dzau V, Braunwald E. Resolved and unresolved issues in the prevention and treatment of coronary artery disease: a workshop consensus statement. Am Heart J. 1991;121(4 Pt 1):1244–63. - PubMed
-
- Dzau VJ, Antman EM, Black HR, Hayes DL, Manson JE, Plutzky J, et al. The cardiovascular disease continuum validated: clinical evidence of improved patient outcomes. Part I: pathophysiology and clinical trial evidence (risk factors through stable coronary artery disease) Circulation. 2006;114:2850–70. - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

