A rapid multiple immunofluorescence method for the simultaneous detection of CD20 and CD3 in canine and feline cytological samples
- PMID: 33814519
- PMCID: PMC8182324
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.20-0597
A rapid multiple immunofluorescence method for the simultaneous detection of CD20 and CD3 in canine and feline cytological samples
Abstract
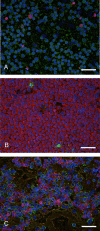
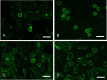
CD20 and CD3 are considered reliable markers for B and T cells, respectively. This study aimed to develop a rapid multiple immunofluorescence (RMIF) method for the detection of CD20 and CD3 on a single cytology slide. Air-dried smears were prepared using samples collected from dogs (n=26) and cats (n=6). Immunosignal detection using the newly developed method required 60 min. Clear immunosignals for CD20 and CD3 were detected in 24 of 26 samples in dogs and in all 6 cats. As the RMIF (CD20/CD3) method can detect markers of both B and T cells simultaneously on a single cytology smear, it would be an efficient tool for the immunophenotyping of canine and feline lymphoma samples.
Keywords: CD20; CD3; immunocytochemistry; immunophenotyping; lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Camus M. S., Kelly L. S., Barger A. M.2020. Immunocytochemistry. pp. 512–20. In: Cowell and Tyler’s Diagnostic Cytology and Hematology of the Dog and Cat, 5th ed. (Valenciano, A. C. and Cowell, R. L. eds.), Elsevier, St. Louis.
-
- Jain S., Aresu L., Comazzi S., Shi J., Worrall E., Clayton J., Humphries W., Hemmington S., Davis P., Murray E., Limeneh A. A., Ball K., Ruckova E., Muller P., Vojtesek B., Fahraeus R., Argyle D., Hupp T. R.2016. The development of a recombinant scFv monoclonal antibody targeting canine CD20 for use in comparative medicine. PLoS One 11: e0148366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148366 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

