Development of Inhalable Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Ciprofloxacin for Noncystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Treatment
- PMID: 33814907
- PMCID: PMC8012696
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S286896
Development of Inhalable Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Ciprofloxacin for Noncystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Treatment
Abstract
Purpose: Ciprofloxacin (CIP) has poor lung targeting after oral inhalation. This study developed optimized inhalable nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for CIP to enhance deposition and accumulation in deeper parts of the lungs for treatment of noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (NCFB).
Methods: NLC formulations based on stearic acid and oleic acid were successfully prepared by hot homogenization and in vitro-characterized. CIP-NLCs were formulated into nanocomposite micro particles (NCMPs) for administration in dry powder inhalation (DPI) formulations by spray-drying (SD) using different ratios of chitosan (CH) as a carrier. DPI formulations were evaluated for drug content and in vitro deposition, and their mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD), fine particle fraction (FPF), fine particle dose (FPD), and emitted dose (ED) were determined.
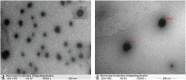
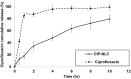
Results: The CIP-NLCs were in the nanometric size range (102.3 ± 4.6 nm), had a low polydispersity index (0.267 ± 0.12), and efficient CIP encapsulation (98.75% ± 0.048%), in addition to a spherical and smooth shape with superior antibacterial activity. The in vitro drug release profile of CIP from CIP-NLCs showed 80% release in 10 h. SD of CIP-NLCs with different ratios of CH generated NCMPs with good yield (>65%). The NCMPs had a corrugated surface, but with increasing lipid:CH ratios, more spherical, smooth, and homogenous NCMPs were obtained. In addition, there was a significant change in the FPF with increasing lipid:CH ratios (P ˂ 0.05). NCMP-1 (lipid:CH = 1:0.5) had the highest FPD (45.0 µg) and FPF (49.2%), while NCMP-3 (lipid:CH = 1:1.5) had the lowest FPF (37.4%). All NCMP powders had an MMAD in the optimum size range of 3.9-5.1 μm.
Conclusion: Novel inhalable CIP NCMP powders are a potential new approach to improved target ability and delivery of CIP for NCFB treatment.
Keywords: DPI; NCFB; NCMPs; NLCs; aerosolization; ciprofloxacin.
© 2021 Almurshedi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Hessah A Aljunaidel is an employee of Novartis. The authors report no other conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

