Lignin: Drug/Gene Delivery and Tissue Engineering Applications
- PMID: 33814908
- PMCID: PMC8009556
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S303462
Lignin: Drug/Gene Delivery and Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
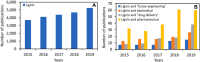
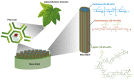
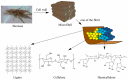
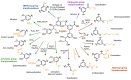
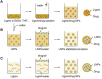
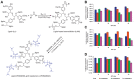
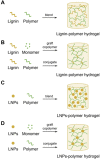
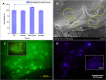
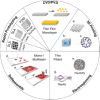
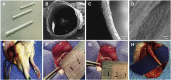
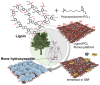
Lignin is an abundant renewable natural biopolymer. Moreover, a significant development in lignin pretreatment and processing technologies has opened a new window to explore lignin and lignin-based bionanomaterials. In the last decade, lignin has been widely explored in different applications such as drug and gene delivery, tissue engineering, food science, water purification, biofuels, environmental, pharmaceuticals, nutraceutical, catalysis, and other interesting low-value-added energy applications. The complex nature and antioxidant, antimicrobial, and biocompatibility of lignin attracted its use in various biomedical applications because of ease of functionalization, availability of diverse functional sites, tunable physicochemical and mechanical properties. In addition to it, its diverse properties such as reactivity towards oxygen radical, metal chelation, renewable nature, biodegradability, favorable interaction with cells, nature to mimic the extracellular environment, and ease of nanoparticles preparation make it a very interesting material for biomedical use. Tremendous progress has been made in drug delivery and tissue engineering in recent years. However, still, it remains challenging to identify an ideal and compatible nanomaterial for biomedical applications. In this review, recent progress of lignin towards biomedical applications especially in drug delivery and in tissue engineering along with challenges, future possibilities have been comprehensively reviewed.
Keywords: biomedical engineering; biopolymer; drug delivery; lignin; nano-biosystem; nanomedicine; tissue engineering.
© 2021 Kumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
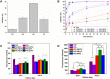
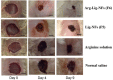
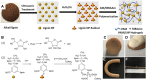
References
-
- Doherty WOS, Mousavioun P, Fellows CM. Value-adding to cellulosic ethanol: lignin polymers. Ind Crops Prod. 2011;33:259–276. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.10.022 - DOI
-
- Figueiredo P, Lintinen K, Hirvonen JT, Kostiainen MA, Santos HA. Properties and chemical modifications of lignin: towards lignin-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2018;93:233–269. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.12.001 - DOI
-
- Adler E. Lignin chemistry-past, present and future. Wood Sci Technol. 1977;11(3):169–218. doi:10.1007/BF00365615 - DOI
-
- Chen H, Gnanasekar P, Nair SS, Xu W, Chauhan P, Yan N. Lignin as a key component in lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils for enhancing the performance of polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate wood adhesives. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2020;8(46):17165–17176. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c05642 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

