Meningeal "Lazarus Response" to Lorlatinib in a ROS1-Positive NSCLC Patient Progressing to Entrectinib
- PMID: 33814929
- PMCID: PMC8009349
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S292730
Meningeal "Lazarus Response" to Lorlatinib in a ROS1-Positive NSCLC Patient Progressing to Entrectinib
Abstract
Background: ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have showed activity and efficacy in ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In the clinical practice, besides the utilization of crizotinib, less is known about the best treatment strategies involving additional, new-generation TKIs for the sequential treatment of ROS1-positive NSCLC patients.
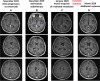
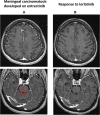
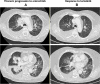
Case presentation: A patient suffering from a ROS1-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma, after receiving cisplatin-pemetrexed chemotherapy, was treated with entrectinib, a new-generation ALK/ROS1/NTRK inhibitor. After 16 months, central nervous system (CNS) metastases appeared, without extra-cerebral disease progression. Stereotactic brain radiotherapy was performed and entrectinib was maintained, due to the global systemic disease control. Approximately one month after radiotherapy, thoracic and meningeal progressions were detected, the latter highly symptomatic with neurocognitive disorders, visual hallucinations and worsening of psycho-motor impairment. A lumbar puncture was positive for tumor cells and for an EZR-ROS1 fusion. The administration of lorlatinib (a third-generation ALK/ROS1 inhibitor) prompted an extremely rapid improvement of clinical conditions, anticipating the positive results observed at radiologic evaluation that confirmed the disease response still ongoing after nine months since treatment start.
Discussion: With the expanding availability of targeted agents with differential activity on resistance mechanism and on CNS disease, choosing wisely the best treatment strategies is pivotal to assure the best clinical outcomes in oncogene-addicted NSCLC patients. Here we have reported lorlatinib reverted an almost fatal meningeal carcinomatosis developing during entrectinib in a ROS1-positive NSCLC patient.
Keywords: CNS; TKI; brain; central nervous system; lung cancer; radiotherapy; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2021 Facchinetti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Facchinetti declares editorial activities sponsored by BMS and Roche. Dr Lavaud declares travel accommodations: Astellas-Pharma, Astra Zeneca, Ipsen, Janssen Oncology, Mundi Pharma. Dr Planchard declares consulting: advisory role or lectures: AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, prIME Oncology, Peer CME, Roche, Samsung Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, prIME Oncology, Peer CME, Roche. Clinical trials research: AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Medimmun, Sanofi-Aventis, Taiho Pharma, Novocure, Daiichi Sankyo. Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer. Pr. Besse declares sponsored research at Gustave Roussy Cancer Center, 4DPharma, Abbvie, Amgen, Aptitude Health, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Cergentis, Cristal Therapeutics, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GSK, Ignyta, IPSEN, Inivata, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Nektar, Onxeo, OSE immunotherapeutics, Pfizer, Pharma Mar, Roche-Genentech, Sanofi, Servier, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Tiziana Pharma, and Tolero Pharmaceuticals. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Entrectinib Response to ROS1-Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer That Progressed on Crizotinib with Leptomeningeal Metastasis: A Case Report.Case Rep Oncol. 2023 Dec 12;16(1):1558-1567. doi: 10.1159/000534549. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38089732 Free PMC article.
-
Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: an international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Dec;18(12):1590-1599. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30680-0. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29074098 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cases of ROS1-rearranged lung cancer: when to use crizotinib, entrectinib, lorlatinib, and beyond?Precis Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;3:17. doi: 10.21037/pcm-2020-potb-02. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Precis Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32776005 Free PMC article.
-
CNS metastasis in ROS1+ NSCLC: An urgent call to action, to understand, and to overcome.Lung Cancer. 2019 Apr;130:201-207. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.02.025. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30885345 Review.
-
Targeted therapies for ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Drugs Today (Barc). 2019 Oct;55(10):641-652. doi: 10.1358/dot.2019.55.10.3030646. Drugs Today (Barc). 2019. PMID: 31720561 Review.
Cited by
-
Repotrectinib's Clinical Benefit and Its Brain Penetration in a Patient with Meningeal Carcinomatosis from G2032R-Mutated ROS-1 Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncol Ther. 2024 Mar;12(1):163-171. doi: 10.1007/s40487-023-00251-6. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Oncol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37973688 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Jun 9;6(2):332-344. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2022.105. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37457125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Entrectinib Response to ROS1-Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer That Progressed on Crizotinib with Leptomeningeal Metastasis: A Case Report.Case Rep Oncol. 2023 Dec 12;16(1):1558-1567. doi: 10.1159/000534549. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38089732 Free PMC article.
-
Complete and durable regression of leptomeningeal involvement during lorlatinib treatment in a patient with lung cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2024 Oct 1;35(9):867-871. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001637. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Anticancer Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39008537 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-1 Fusions in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence to Date.Curr Oncol. 2022 Jan 28;29(2):641-658. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29020057. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35200557 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

