Agnuside Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis through the Inhibition of HIF-1 α and NLRP3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 33814979
- PMCID: PMC7987448
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5534614
Agnuside Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis through the Inhibition of HIF-1 α and NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
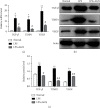
Increasing evidence has shown that NLRP3 inflammasome activation participates in chronic aseptic inflammation and is related to tissue fibrosis. Our last study also revealed the vital role of NLRP3 inflammasome, highly associated with tissue hypoxia, in the onset and development of knee osteoarthritis (KOA). In this study, we tried to find a possible benign intervention for that pathological process. Agnuside (AGN), a nontoxic, natural small molecule isolated from the extract of Vitex negundo L. (Verbenaceae), has been demonstrated to have antioxidation, anti-inflammatory, analgesia, and many other properties as an iridoid glycoside, although its specific target is still unclear. Therefore, we established MIA-induced KOA model rats and investigated the effects of AGN oral gavage on oxygen-containing state, NLRP3 inflammasome, synovitis, and fibrosis in KOA. Pimonidazole staining and HIF-1α immunohistochemical assay both showed that AGN at the oral dose of 6.25 mg/kg can effectively relieve local hypoxia in synovial tissue. Besides, we observed a decrease of HIF-1α, caspase-1, ASC, and NLRP3 after AGN intervention, both in the mRNA and protein levels. In addition, rats treated with the AGN showed less inflammatory reaction and fibrosis, not only in the expression of NLRP3, inflammasome downstream factors IL-1β and IL-18, and fibrosis markers TGF-β, TIMP1, and VEGF but also in the observation of HE staining, anatomical characteristics, Sirius Red staining, and type I collagen immunohistochemistry. Subsequently, we established LPS-induced models of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) mimicking the inflammatory environment of KOA and activating NLRP3 inflammasome. FLSs treated with AGN (3 μM) resulted in a downregulation of HIF-1α and the components required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Meanwhile, the content of proinflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-18 in FLS supernatant was also reduced by AGN. In addition, both mRNA and protein levels of the fibrotic markers were significantly decreased after AGN management. To conclude, this study demonstrates that AGN alleviates synovitis and fibrosis in experimental KOA through the inhibition of HIF-1α accumulation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Additionally, not only does it reveal some novel targets for anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of AGN but also announces its potential value in treating KOA in humans.
Copyright © 2021 Li Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest, including any financial, personal, or other relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence, or be perceived to influence our work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Casticin suppresses monoiodoacetic acid-induced knee osteoarthritis through inhibiting HIF-1α/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Sep;86:106745. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106745. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32622201
-
Chrysin Attenuates the NLRP3 Inflammasome Cascade to Reduce Synovitis and Pain in KOA Rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jul 28;14:3015-3027. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S261216. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32801641 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Synovial Macrophage Pyroptosis Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Sep 8;2019:2165918. doi: 10.1155/2019/2165918. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31582897 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome intervention for synovitis in knee osteoarthritis: A review of TCM intervention.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 29;14:1159167. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1159167. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37065495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism and Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome during Fibrosis.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 26;12(5):634. doi: 10.3390/biom12050634. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625564 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Potentiality of Bioactive Substances: Regulating the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Autoimmune Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 28;15(21):4584. doi: 10.3390/nu15214584. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting inflammasome-dependent mechanisms as an emerging pharmacological approach for osteoarthritis therapy.iScience. 2022 Nov 11;25(12):105548. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105548. eCollection 2022 Dec 22. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36465135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the extracellular matrix in non-cartilage soft-tissues in osteoarthritis: a systematic review.Bone Joint Res. 2024 Dec 3;13(12):703-715. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1312.BJR-2024-0020.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2024. PMID: 39622273 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Comprehensive Review on Flavonoid-Based Interventions.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb 19. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01696-4. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39966334 Review.
-
Clinical effect of glucosamine hydrochloride combined with compound osteopeptide injection for knee osteoarthritis.Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Nov-Dec;39(6):1809-1813. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.6.8151. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37936773 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

