Mucosal Epithelial Jak Kinases in Health and Diseases
- PMID: 33814980
- PMCID: PMC7990561
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6618924
Mucosal Epithelial Jak Kinases in Health and Diseases
Abstract
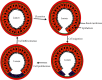
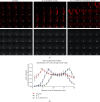
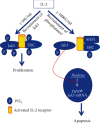
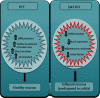
Janus kinases (Jaks) are a family of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase that include four different members, viz., Jak1, Jak2, Jak3, and Tyk2. Jaks play critical roles in immune cells functions; however, recent studies suggest they also play essential roles in nonimmune cell physiology. This review highlights the significance of epithelial Jaks in understanding the molecular basis of some of the diseases through regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell survival, cell growth, development, and differentiation. Growth factors and cytokines produced by the cells of hematopoietic origin use Jak kinases for signal transduction in both immune and nonimmune cells. Among Jaks, Jak3 is widely expressed in both immune cells and in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) of both humans and mice. Mutations that abrogate Jak3 functions cause an autosomal severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) while activating Jak3 mutations lead to the development of hematologic and epithelial cancers. A selective Jak3 inhibitor CP-690550 (Xeljanz) approved by the FDA for certain chronic inflammatory conditions demonstrates immunosuppressive activity in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and organ transplant rejection. Here, we also focus on the consequences of Jak3-directed drugs on adverse effects in light of recent discoveries in mucosal epithelial functions of Jak3 with some information on other Jaks. Lastly, we brief on structural implications of Jak3 domains beyond the immune cells. As information about the roles of Jak3 in gastrointestinal functions and associated diseases are only just emerging, in the review, we summarize its implications in gastrointestinal wound repair, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity-associated metabolic syndrome, and epithelial cancers. Lastly, we shed lights on identifying potential novel targets in developing therapeutic interventions of diseases associated with dysfunctional IEC.
Copyright © 2021 Narendra Kumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures
References
-
- Candotti F., Oakes S. A., Johnston J. A., Notarangelo L. D., O'Shea J. J., Blaese R. M. In vitro correction of JAK3-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency by retroviral-mediated gene transduction. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1996;183(6):2687–2692. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2687. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Safford M. G., Levenstein M., Tsifrina E., et al. JAK3: expression and mapping to chromosome 19p12-13.1. Experimental Hematology. 1997;25(5):374–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

