Comparative Analysis of Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev (Hemiptera: Miridae) Immune Responses to Fungal and Bacterial Pathogens
- PMID: 33815150
- PMCID: PMC8012897
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.646721
Comparative Analysis of Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev (Hemiptera: Miridae) Immune Responses to Fungal and Bacterial Pathogens
Abstract
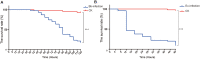
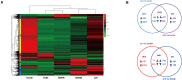
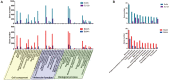
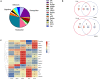
The wide-spread culture of transgenic Bt cotton resisting the infamous cotton bollworms has reduced the adoption of broad-spectrum insecticides to a large extent. Consequently, the non-targeted insect Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev has become a major cotton pest in China. Entomopathogenic microbes show promising results for controlling this pest in the future, but A. suturalis innate immune responses to these pathogens are poorly understood. Here, we used the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and the Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria Enterobactor cloacae to infect A. suturalis nymphs, followed by high throughput RNA-seq to analyze the immune transcriptomes of A. suturalis in response to the two pathogens. A total of 150 immunity-related genes were identified, including pattern recognition receptors, extracellular signal modulators, signal pathways (Toll, IMD, JNK, and JAK/STAT), and response effectors. Further quantitative real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that B. bassiana and E. cloacae were recognized by different receptors (GNBP and PGRP, respectively); activated Toll pathway and IMD pathway respectively; and both induced expression of the effector gene Defensin. However, melanization is suppressed in B. bassiana-infected nymphs. Collectively, this study provides a transcriptomic snapshot of the A. suturalis immune system, and at the genetic level, gains multifaceted insights of the immune response to fungal and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Ultimately this work pioneers the study of molecular mechanisms underlying immune interactions between A. suturalis and its pathogens and assists in the development of novel mitigation strategies to control this pest.
Keywords: Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev; Beauveria bassiana; Enterobactor cloacae; RNA-seq; immune system.
Copyright © 2021 Ma, Guo, Tu, Wang, Xu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated Omics Analysis Reveals Key Pathways in Cotton Defense against Mirid Bug (Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev) Feeding.Insects. 2024 Apr 8;15(4):254. doi: 10.3390/insects15040254. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38667384 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput profiling of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera immunotranscriptome during the fungal and bacterial infections.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 18;16(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1509-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26001831 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of AsAP in the Reproduction of Adelphocoris suturalis (Hemiptera: Miridae).Insects. 2022 Aug 22;13(8):755. doi: 10.3390/insects13080755. Insects. 2022. PMID: 36005380 Free PMC article.
-
Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future.J Invertebr Pathol. 2015 Nov;132:1-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Invertebr Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26225455 Review.
-
[Progress in innate immunity-related genes in insects].Yi Chuan. 2018 Jun 20;40(6):451-466. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-363. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 29959118 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Gut Bacterial Diversity in Different Life Cycle Stages of Adelphocoris suturalis (Hemiptera: Miridae).Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 2;12:670383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.670383. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34149656 Free PMC article.
-
Aedes aegypti Beta-1,3-Glucan-Binding Protein Inhibits Dengue and ZIKA Virus Replication.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 1;12(1):88. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010088. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255195 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Omics Analysis Reveals Key Pathways in Cotton Defense against Mirid Bug (Adelphocoris suturalis Jakovlev) Feeding.Insects. 2024 Apr 8;15(4):254. doi: 10.3390/insects15040254. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38667384 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 35 C-Type Lectins in the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker).Insects. 2021 Jun 16;12(6):559. doi: 10.3390/insects12060559. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34208748 Free PMC article.
-
The Intestinal Immune Defense System in Insects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 1;23(23):15132. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315132. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cerenius L., Söderhäll K. (2004). The prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 198 116–126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

