Novel Compound Heterozygous Pathogenic Mutations of SLC5A5 in a Chinese Patient With Congenital Hypothyroidism
- PMID: 33815280
- PMCID: PMC8018529
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.620117
Novel Compound Heterozygous Pathogenic Mutations of SLC5A5 in a Chinese Patient With Congenital Hypothyroidism
Abstract
Background and objectives: Defects in the human sodium/iodide symporter (SLC5A5) gene have been reported to be one of the causes of congenital hypothyroidism (CH). We aimed to identify SLC5A5 mutations in Chinese patients with CH and to evaluate the function of the mutation.
Methods: Two hundred and seventy-three patients with primary CH were screened for mutations in SLC5A5 using next-generation sequencing. We investigated the expression and cellular localization of the novel compound heterozygous mutation in SLC5A5. The functional activity of the mutants was further examined in vitro.
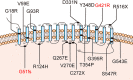
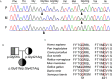
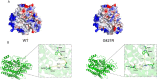
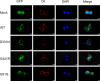
Results: In 273 patients with CH, two previously undescribed pathogenic mutations p.Gly51AlafsTer45 (G51fs) and p.Gly421Arg (G421R) in a compound heterozygous state in SLC5A5 were identified in a pediatric patient. G51fs was located in the first intercellular loop connecting transmembrane segment I and II, whereas G421R was in the transmembrane segment (TMS) XI. G51fs and G421R resulted in a truncated NIS and reduced protein expression, respectively. In vitro experiments further showed that the normal function of iodine transport of sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) mutants was markedly impaired.
Conclusion: The undescribed compound heterozygous mutation of SLC5A5 was discovered in a Chinese CH patient. The mutation led to significantly reduced NIS expression and impaired iodide transport function accompanied by the impaired location of the NIS on the plasma membrane. Our study thus provides further insights into the roles of SLC5A5 in CH pathogenesis.
Keywords: SLC5A5; congenital hypothyroidism; iodine transport; mutation; next-generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Cheng, Zhang, Fang, Wang, Wu, Li, Liang, Li and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
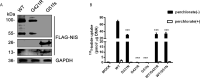
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

