Indole Inhibits IncP-1 Conjugation System Mainly Through Promoting korA and korB Expression
- PMID: 33815310
- PMCID: PMC8017341
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.628133
Indole Inhibits IncP-1 Conjugation System Mainly Through Promoting korA and korB Expression
Abstract
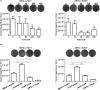
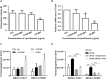
Indole works as an interspecies signal molecule to regulate multiple physiological activities, like antibiotic resistance, acid resistance, and virulence. However, the effect of indole on conjugation is unknown. Here, with Escherichia coli SM10λπ as a donor strain that carries a chromosomally integrated conjugative RP4 plasmid, we explored the effect of indole on conjugation of a mobilizable pUCP24T plasmid imparting gentamycin resistance. The results showed that exogenous indole treatment inhibited conjugative transfer of pUCP24T from SM10λπ to recipient strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and E. coli EC600. Furthermore, raising endogenous indole production through overexpression of TnaA, a tryptophanase, in SM10λπ significantly inhibited both SM10λπ-PAO1 and SM10λπ-EC600 conjugation, whereas deficiency of tnaA reversed the phenotype. Subsequent mechanistic studies revealed that exogenous indole significantly inhibited the expression of mating pair formation gene (trbB) and the DNA transfer and replication gene (trfA), mainly due to the promotion of regulatory genes (korA and korB), and the result was confirmed in tnaA knockout and overexpression strains. Additionally, we found that both extracellular indole production and tnaA expression of SM10λπ were downregulated by ciprofloxacin (CIP). Intriguingly, one-eighth minimum inhibitory concentration of CIP treatment clearly facilitated both SM10λπ-PAO1 and SM10λπ-EC600 conjugation, and indole inhibited CIP-induced conjugation frequency. These data suggest that indole may play a negative role in the process of CIP-induced conjugation. This is the first study to reveal the biological function of indole-inhibiting conjugation and its role in CIP-induced conjugation, which may be developed into a new way of controlling the spread of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: E. coli; antibiotic resistance; ciprofloxacin; conjugation; indole.
Copyright © 2021 Xiong, Liu, Pu, Liu, Zheng, Zeng, Chen, Lu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
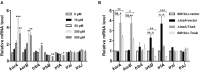
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

