β-Hexosaminidases Along the Secretory Pathway of Nicotiana benthamiana Have Distinct Specificities Toward Engineered Helminth N-Glycans on Recombinant Glycoproteins
- PMID: 33815445
- PMCID: PMC8010188
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.638454
β-Hexosaminidases Along the Secretory Pathway of Nicotiana benthamiana Have Distinct Specificities Toward Engineered Helminth N-Glycans on Recombinant Glycoproteins
Abstract
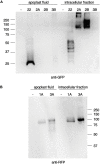
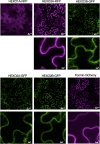
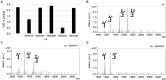
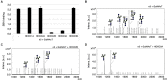
Secretions of parasitic worms (helminths) contain a wide collection of immunomodulatory glycoproteins with the potential to treat inflammatory disorders, like autoimmune diseases. Yet, the identification of single molecules that can be developed into novel biopharmaceuticals is hampered by the limited availability of native parasite-derived proteins. Recently, pioneering work has shown that helminth glycoproteins can be produced transiently in Nicotiana benthamiana plants while simultaneously mimicking their native helminth N-glycan composition by co-expression of desired glycosyltransferases. However, efficient "helminthization" of N-glycans in plants by glyco-engineering seems to be hampered by the undesired truncation of complex N-glycans by β-N-acetyl-hexosaminidases, in particular when aiming for the synthesis of N-glycans with antennary GalNAcβ1-4GlcNAc (LacdiNAc or LDN). In this study, we cloned novel β-hexosaminidase open reading frames from N. benthamiana and characterized the biochemical activity of these enzymes. We identified HEXO2 and HEXO3 as enzymes responsible for the cleavage of antennary GalNAc residues of N-glycans on the model helminth glycoprotein kappa-5. Furthermore, we reveal that each member of the HEXO family has a distinct specificity for N-glycan substrates, where HEXO2 has strict β-galactosaminidase activity, whereas HEXO3 cleaves both GlcNAc and GalNAc. The identification of HEXO2 and HEXO3 as major targets for LDN cleavage will enable a targeted genome editing approach to reduce undesired processing of these N-glycans. Effective knockout of these enzymes could allow the production of therapeutically relevant glycoproteins with tailor-made helminth N-glycans in plants.
Keywords: LacdiNAc; N-glycosylation; Nicotiana benthamiana; glyco-engineering; β-hexosaminidases.
Copyright © 2021 Alvisi, van Noort, Dwiani, Geschiere, Sukarta, Varossieau, Nguyen, Strasser, Hokke, Schots and Wilbers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

