Method for Essential Protein Prediction Based on a Novel Weighted Protein-Domain Interaction Network
- PMID: 33815480
- PMCID: PMC8010314
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.645932
Method for Essential Protein Prediction Based on a Novel Weighted Protein-Domain Interaction Network
Abstract
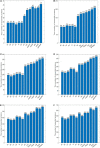
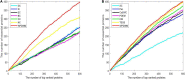
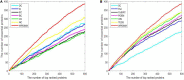
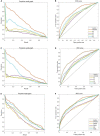
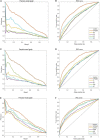
In recent years a number of calculative models based on protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks have been proposed successively. However, due to false positives, false negatives, and the incompleteness of PPI networks, there are still many challenges affecting the design of computational models with satisfactory predictive accuracy when inferring key proteins. This study proposes a prediction model called WPDINM for detecting key proteins based on a novel weighted protein-domain interaction (PDI) network. In WPDINM, a weighted PPI network is constructed first by combining the gene expression data of proteins with topological information extracted from the original PPI network. Simultaneously, a weighted domain-domain interaction (DDI) network is constructed based on the original PDI network. Next, through integrating the newly obtained weighted PPI network and weighted DDI network with the original PDI network, a weighted PDI network is further constructed. Then, based on topological features and biological information, including the subcellular localization and orthologous information of proteins, a novel PageRank-based iterative algorithm is designed and implemented on the newly constructed weighted PDI network to estimate the criticality of proteins. Finally, to assess the prediction performance of WPDINM, we compared it with 12 kinds of competitive measures. Experimental results show that WPDINM can achieve a predictive accuracy rate of 90.19, 81.96, 70.72, 62.04, 55.83, and 51.13% in the top 1%, top 5%, top 10%, top 15%, top 20%, and top 25% separately, which exceeds the prediction accuracy achieved by traditional state-of-the-art competing measures. Owing to the satisfactory identification effect, the WPDINM measure may contribute to the further development of key protein identification.
Keywords: computational model; domain-domain interaction network; essential proteins; protein-domain interaction network; protein-protein interaction network.
Copyright © 2021 Meng, Kuang, Chen, Zhang, Tan, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor QZ declared a past co-authorship/collaboration with one of the authors LW.
Figures


References
-
- Bateman A., Coin L., Durbin R., Finn R. D., Hollich V., Griffithsjones S., et al. (2004). The pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 42 D222–D230.
-
- Bonacich P. (1987). Power and centrality: a family of measures. Am. J. Sociol. 92 1170–1182. 10.2307/2780000 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

