Long non-coding RNA receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 33815591
- PMCID: PMC8014969
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9949
Long non-coding RNA receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Long non‑coding RNA receptor activator of nuclear factor‑κB ligand promotes cisplatin resistance in non‑small cell lung cancer cells.Exp Ther Med. 2024 May 1;28(1):272. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12560. eCollection 2024 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38765655 Free PMC article.
Abstract
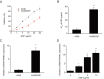
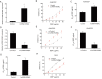
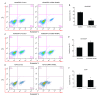
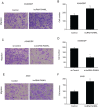
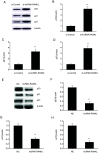
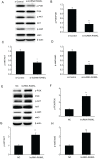
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a common malignancy associated with poor clinical outcomes and high mortality rate. The association between NSCLC development and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) expression remains to be elucidated. The current study investigated the role of a novel lncRNA, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand (RANKL), in the resistance of NSCLC to chemotherapy. RANKL expression was assessed via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, cell death rate was evaluated using flow cytometry and sensitivity of cisplatin (DDP)-resistant A549/DDP cells to chemotherapy was determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Western blotting was performed to quantify p53 protein levels. Compared with matched A549 cells, A549/DDP cells exhibited significant upregulation of RANKL expression. Sensitivity of A549/DDP cells to DDP was restored following RANKL knockdown. A549 cells overexpressing RANKL exhibited notably impaired DDP sensitivity compared with controls. Conversely, downregulated RANKL expression triggered cell death and inhibited cell migration via p53 stimulation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway suppression. The current findings indicate that RANKL contributes to DDP resistance in NSCLC and may represent a novel therapeutic target in this malignancy.
Keywords: cisplatin resistance; long non-coding RNA receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand; non-small-cell lung cancer; p53.
Copyright: © Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wong ML, McMurry TL, Stukenborg GJ, Francescatti AB, Amato-Martz C, Schumacher JR, Chang GJ, Greenberg CC, Winchester DP, McKellar DP, et al. Impact of age and comorbidity on treatment of non-small cell lung cancer recurrence following complete resection: A nationally representative cohort study. Lung Cancer. 2016;102:108–117. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.11.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu HF, Liu JS, Deng JH, Wu RR. Role of XRCC1 gene polymorphisms in non-small cell lung cancer cisplatin-based chemotherapy, and their effect on clinical and pathological characteristics. Genet Mol Res: 15, 2016 doi: 10.4238/gmr15049084. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
