Impact of adipose tissue in chronic kidney disease development (Review)
- PMID: 33815612
- PMCID: PMC8014972
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9969
Impact of adipose tissue in chronic kidney disease development (Review)
Abstract
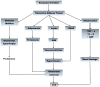
Obesity is a worldwide pandemic health issue. Obesity is associated with the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and kidney diseases. This systemic disease can affect the kidneys by two mechanisms: Indirectly through diabetes mellitus (DM) and hypertension and directly through adipokines secreted by adipose tissue. Obesity is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality among the adult population. Increased visceral adipose tissue leads to renal glomerular hyperfiltration and hyperperfusion, which may lead to glomerular hypertrophy, proteinuria, and CKD development. Adipokines are hormones produced by fat tissue. They are involved in energy homeostasis, sugar and fat metabolism, reproduction, immunity, and thermogenesis control. Hormones and cytokines secreted by adipose tissue contribute to the development and progression of CKD. Decreased serum or urinary adiponectin levels are specific in diabetic and non-diabetic CKD patients, while leptin presents increased levels, and both are associated with the development of glomerulopathy. Excessive adipose tissue is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress (OS), insulin resistance and activation of the renin angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Therefore, adipose tissue dysfunction plays an important role in the development of CKD.
Keywords: adipokines; chronic kidney disease; endocrine organ; glomerulopathy; inflammation; obesity.
Copyright: © Miricescu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrition and Obesity Impacts on Kidney Health.Contrib Nephrol. 2021;199:24-42. doi: 10.1159/000517669. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Contrib Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34343991 Review.
-
Adipose tissue metabolic changes in chronic kidney disease.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023 Apr 27;5(2):e00023. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000023. eCollection 2023 Apr. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023. PMID: 37128293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal disease in obesity: the need for greater attention.J Ren Nutr. 2006 Jul;16(3):216-23. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2006.04.017. J Ren Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16825023 Review.
-
Obesity associated hypertension: new insights into mechanism.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013 Dec;11(2):46-52. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2013.11.2.46. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013. PMID: 24627704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity, kidney dysfunction, and inflammation: interactions in hypertension.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Jul 7;117(8):1859-1876. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa336. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33258945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Interplay Between SARS-CoV-2 and Renal Impairment.Cureus. 2024 Aug 10;16(8):e66553. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66553. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39252712 Free PMC article.
-
The Causes and Potential Injurious Effects of Elevated Serum Leptin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4685. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094685. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of COVID-19 Infection on Liver Transplant Recipients: Does It Make Any Difference?Cureus. 2022 Feb 28;14(2):e22687. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22687. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35386162 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Syndrome-Related Kidney Injury: A Review and Update.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 23;13:904001. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.904001. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35813613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weight Loss Supplements.Molecules. 2023 Jul 12;28(14):5357. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145357. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mandita A, Timofte D, Balcangiu-Stroescu AE, Balan D, Raducu L, Tanasescu MD, Diaconescu A, Dragos D, Cosconel CI, Stoicescu SM, Ionescu D. Treatment of high blood pressure in patients with chronic renal disease. Rev Chim Buchar. 2019;70:993–995.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources