Impact of oral L-arginine supplementation on blood pressure dynamics in children with severe sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis
- PMID: 33815929
- PMCID: PMC8012291
Impact of oral L-arginine supplementation on blood pressure dynamics in children with severe sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis
Abstract
Sickle cell anaemia (SCA) patients generally have lower blood pressures compared to those with the AA haemoglobin genotype. However, during vaso-occlusive crises (SCA-VOC), blood pressures (BP) may elevate transiently to levels beyond the 95th percentile. The risk of stroke or even death increases with increasing systolic BP in SCA. Therefore, interventions targeted at BP reduction may be essential during severe vaso-occlusive episodes. Reduction in BP was achieved with arginine therapy in a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCT) in non-sickle cell adults. The impact of oral arginine (given for pain control) on the BP of children with SCA-VOC has not been documented.
Methods: A double-blind RCT of oral L-arginine hydrochloride as adjuvant therapy for pain reduction was conducted in children with SCA-VOC, aged 5-17 years, over a 2-year period. The mean change in BP and the time to achieve BP <90th percentile was added as part of the outcome variables. The anthropometry, pain scores and mercury sphygmomanometry were done following standard procedures. BP percentiles were generated using the Fourth Report guidelines. Differences in the time to normalization of BP in the treatment arms were tested with Kaplan-Meier analysis.
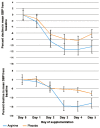
Results: Sixty-six children (57.6% male) were randomized into L-arginine (35 patients) or placebo (31 patients) arm. The prevalence of hypertension (BP ≥95th percentile) at presentation tended to increase as the pain scores increased, from a prevalence of 50% in patients with a score of 7 to 65% in those with score of 10 (systolic hypertension) and from 44.4% in patients with pain score of 7 to 50% in patients with pain score of 10 (diastolic hypertension). Patients that received arginine recorded a 12.8±3.2 mmHg decline in mean systolic BP compared to the placebo group, where a mean difference of 7.6±1.5 mmHg was observed, P<0.001. Similarly, the mean diastolic BP reduced by 13% in the arginine group and 7.5% in the placebo group, P<0.001. Children who received arginine tended to achieve BP normalization much faster than the placebo group (P=0.112), and no serious adverse events were documented related to the hypertension or arginine administration.
Conclusions: High blood pressure (≥95th percentile) is common amongst children with SCA-VOC and are mostly asymptomatic. Administration of oral arginine given for pain control achieves a reduction of the BP at a faster rate in children compared to placebo and it is safe.
Keywords: Nigerian children; Oral arginine; blood pressure; sickle cell anemia.
AJCD Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Randomized control trial of oral arginine therapy for children with sickle cell anemia hospitalized for pain in Nigeria.Am J Hematol. 2021 Jan;96(1):89-97. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26028. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Am J Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33075179 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma L-Arginine in Sickle Cell Anaemia Patients in Crises and its Correlation with Markers of Severity of Disease.West Afr J Med. 2021 Apr 23;38(4):366-373. West Afr J Med. 2021. PMID: 33902958
-
Myocardial injury in patients with sickle cell anaemia and myocardial ischaemia in Calabar, Nigeria.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2020 Nov;40(4):231-237. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1789398. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2020. PMID: 32662752
-
Magnesium for treating sickle cell disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 9;9(9):CD011358. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011358.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31498421 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oral L-arginine supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials.Am Heart J. 2011 Dec;162(6):959-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.09.012. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Am Heart J. 2011. PMID: 22137067 Review.
Cited by
-
Blood pressure and electrocardiographic profile of children with sickle cell anaemia in steady-state and vaso-occlusive crisis.Ghana Med J. 2023 Sep;57(3):183-190. doi: 10.4314/gmj.v57i3.4. Ghana Med J. 2023. PMID: 38957667 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine Therapy for Pain in Sickle Cell Disease: A Phase-2 Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Am J Hematol. 2025 Jul;100(7):1119-1131. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27692. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Am J Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40270092 Clinical Trial.
-
Sickle Cell Disease.Transfus Med Hemother. 2024 Aug 6;51(5):332-344. doi: 10.1159/000540149. eCollection 2024 Oct. Transfus Med Hemother. 2024. PMID: 39371249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of l-arginine supplementation in patients with sickle cell disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 11;6(4):e1167. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1167. eCollection 2023 Apr. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37064309 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine Therapy and Cardiopulmonary Hemodynamics in Hospitalized Children with Sickle Cell Anemia: A Prospective, Double-blinded, Randomized Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Jul 1;206(1):70-80. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202108-1930OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35426778 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
