Dual-energy computed tomography could reliably differentiate metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes of less than 0.5 cm in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 33816174
- PMCID: PMC7930679
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-846
Dual-energy computed tomography could reliably differentiate metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes of less than 0.5 cm in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) has been widely applied to detect lymph node (LN) and lymph node metastasis (LNM) in various cancers, including papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). This study aimed to quantitatively evaluate metastatic cervical lymph nodes (LNs) <0.5 cm in patients with PTC using DECT, which has not been done in previous studies.
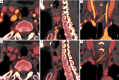
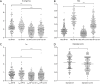
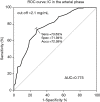
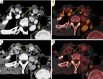
Methods: Preoperative DECT data of patients with pathologically confirmed PTC were retrospectively collected and analyzed between May 2016 and June 2018. A total of 359 LNs from 52 patients were included. Diameter, iodine concentration (IC), normalized iodine concentration (NIC), and the slope of the energy spectrum curve (λHU) of LNs in the arterial and the venous phases were compared between metastatic and non-metastatic LNs. The optimal parameters were obtained from the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The generalized estimation equation (GEE) model was used to evaluate independent diagnostic factors for LNM.
Results: A total of 139 metastatic and 220 non-metastatic LNs were analyzed. There were statistical differences of quantitative parameters between the two groups (P value 0.000-0.007). The optimal parameter for diagnosing LNM was IC in the arterial phase, and its area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity were 0.775, 71.9%, and 73.6%, respectively. When the three parameters of diameter, IC in the arterial phase, and NIC in the venous phase were combined, the prediction efficiency was better, and the AUC was 0.819. The GEE results showed that LNs located in level VIa [odds ratio (OR) 2.030, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.134-3.634, P=0.017], VIb (OR 2.836, 95% CI: 1.597-5.038, P=0.000), diameter (OR 2.023, 95% CI: 1.158-3.532, P=0.013), IC in the arterial phase (OR 4.444, 95% CI: 2.808-7.035, P=0.000), and IC in the venous phase (OR 5.387, 95% CI: 3.449-8.413, P=0.000) were independent risk factors for LNM in patients with PTC.
Conclusions: DECT had good diagnostic performance in the differentiation of cervical metastatic LNs <0.5 cm in patients with PTC.
Keywords: Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC); dual-energy computed tomography (DECT); iodine concentration (IC); lymph nodes (LNs); metastasis.
2021 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-846). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Hashimoto's thyroiditis on the dual-energy CT quantitative parameters and performance in diagnosing metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid cancer.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Jan 18;24(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00655-1. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38238870 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of lymph node metastases in patients with ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma: Incremental diagnostic value of dual-energy CT combined with morphologic parameters.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Jun;187:112107. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.112107. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40222185
-
Diagnostic accuracy of single-source dual-energy computed tomography and ultrasonography for detection of lateral cervical lymph node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Dec;11(12):5032-5041. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.12.45. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 32030219 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) quantitative parameters for detecting metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Feb;183:111917. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.111917. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39778378
-
The accuracy of ultrasonography in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2012 Aug;81(8):1798-805. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.04.028. Epub 2011 May 4. Eur J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 21536396 Review.
Cited by
-
Value of dual-layer spectral detector CT in predicting lymph node metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):749-764. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-447. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223109 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the preoperative evaluation of lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a single-center retrospective study.BMC Surg. 2023 Oct 24;23(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02199-w. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37875825 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of dual-layer CT in the assessment of lymph nodes in lymphoma patients with PET/CT as a reference standard.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 26;13(1):18323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45198-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37884597 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of virtual noncontrast images to remove intrinsic and external iodine from the thyroid via dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Dec 5;14(12):9486-9496. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-116. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39698602 Free PMC article.
-
Mono+ algorithm assessment of the diagnostic value of dual-energy CT for high-risk factors for colorectal cancer: a preliminary study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):432-446. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-291. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carling T, Carty SE, Ciarleglio MM, Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Kim LT, Kloos RT, Mazzaferri EL, Sr, Peduzzi PN, Roman SA, Sippel RS, Sosa JA, Stack BC, Jr, Steward DL, Tufano RP, Tuttle RM, Udelsman R. American Thyroid Association design and feasibility of a prospective randomized controlled trial of prophylactic central lymph node dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2012;22:237-44. 10.1089/thy.2011.0317 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lesnik D, Cunnane ME, Zurakowski D, Acar GO, Ecevit C, Mace A, Kamani D, Randolph GW. Papillary thyroid carcinoma nodal surgery directed by a preoperative radiographic map utilizing CT scan and ultrasound in all primary and reoperative patients. Head Neck 2014;36:191-202. 10.1002/hed.23277 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
