YBX3 Mediates the Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma via PI3K/AKT Signaling
- PMID: 33816248
- PMCID: PMC8010247
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.617621
YBX3 Mediates the Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma via PI3K/AKT Signaling
Abstract
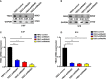
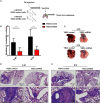
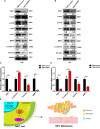
The metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a complex process associated with oncogenic dysfunction, the deciphering of which remains a challenge and requires more in-depth studies. Y-box protein 3 (YBX3) is a DNA/RNA binding protein associated with gene transcription, DNA repair, and the progression of various diseases. However, whether and how YBX3 affects the metastasis of NPC remains unknown. Thus, in this study, we aimed to investigate the role of YBX3 in the metastasis of NPC and determine its underlying mechanism. Interestingly, it was found that the expression of YBX3, which was associated with NPC metastasis, was upregulated in the clinical NPC tissues and cell lines. Moreover, we found that knockdown of YBX3 expression by lentivirus shRNA significantly suppressed NPC cells migration in vitro and metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, RNA sequencing results suggested that the genes regulated by YBX3 were significantly enriched in cell adhesion molecules, cAMP signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, focal adhesion, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, Rap1 signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, and Chemokine signaling pathway. Of these, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway contained the most genes. Accordingly, YBX3 knockdown decreased the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby inhibit epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and MMP1. These results have demonstrated that YBX3 are involved in the metastasis of NPC through regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and serve as a potential therapeutic target for patients with NPC.
Keywords: MMP1; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; Y-box protein 3; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); nasopharyngeal carcinoma; tumor metastasis.
Copyright © 2021 Fan, Xie, Yang, Wang, Wu, Deng, Weng, Wen and Nie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

