Characteristics of Viral Shedding Time in SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33816427
- PMCID: PMC8017277
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.652842
Characteristics of Viral Shedding Time in SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
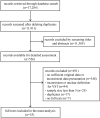
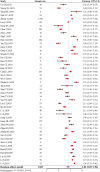
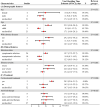
Background: The viral shedding time (VST) of SARS-CoV-2 mainly determines its transmission and duration of infectiousness. However, it was heterogeneous in the existing studies. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to comprehensively summarize the VST of SARS-CoV-2. Methods: We searched PubMed, Web of Science, MedRxiv, BioRxiv, CNKI, CSTJ, and Wanfang up to October 25, 2020, for studies that reported VSTs of SARS-CoV-2. Pooled estimates and 95% CIs for the VSTs were calculated using log-transformed data. The VSTs in SARS-CoV-2 infections based on different demographic and clinical characteristics, treatments and specimens were stratified by subgroup analysis. Results: A total of 35 studies involving 3,385 participants met the inclusion criteria. The pooled mean VST was 16.8 days (95% CI: 14.8-19.4, I2 = 99.56%) in SARS-CoV-2 infections. The VST was significantly longer in symptomatic infections (19.7 days, 95% CI: 17.2-22.7, I2 = 99.34%) than in asymptomatic infections (10.9 days, 95% CI: 8.3-14.3, I2 = 98.89%) (P < 0.05). The VST was 23.2 days (95% CI: 19.0-28.4, I2 = 99.24%) in adults, which was significantly longer than that in children (9.9 days, 95% CI: 8.1-12.2, I2 = 85.74%) (P < 0.05). The VST was significantly longer in persons with chronic diseases (24.2 days, 95% CI: 19.2-30.2, I2 = 84.07%) than in those without chronic diseases (11.5 days, 95% CI: 5.3-25.0, I2 = 82.11%) (P < 0.05). Persons receiving corticosteroid treatment (28.3 days, 95% CI: 25.6-31.2, I2 = 0.00%) had a longer VST than those without corticosteroid treatment (16.2 days, 95% CI: 11.5-22.5, I2 = 92.27%) (P = 0.06). The VST was significantly longer in stool specimens (30.3 days, 95% CI: 23.1-39.2, I2 = 92.09%) than in respiratory tract specimens (17.5 days, 95% CI: 14.9-20.6, I2 = 99.67%) (P < 0.05). Conclusions: A longer VST was found in symptomatic infections, infected adults, persons with chronic diseases, and stool specimens.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS- CoV-2; meta-analysis; systematic review; viral shedding time.
Copyright © 2021 Yan, Zhang, Chen, Jiang, Liu, Zhou, Huang, Zhou, Guan, Ding, Chen, Lan, Fu, Wu, Li and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
In patients with COVID-19, viral shedding time is 17 d and varies in some subgroups.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Aug;174(8):JC94. doi: 10.7326/ACPJ202108170-094. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34339222
References
-
- World Coronavirus Death . Coronavirus Death Toll and Trends –Worldometer. (2020). Available online at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus (accessed February 4, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

