Strength Through Unity: The Power of the Mega-Scaffold MACF1
- PMID: 33816492
- PMCID: PMC8012552
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641727
Strength Through Unity: The Power of the Mega-Scaffold MACF1
Abstract
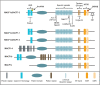
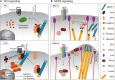
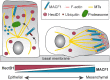
The tight coordination of diverse cytoskeleton elements is required to support several dynamic cellular processes involved in development and tissue homeostasis. The spectraplakin-family of proteins are composed of multiple domains that provide versatility to connect different components of the cytoskeleton, including the actin microfilaments, microtubules and intermediates filaments. Spectraplakins act as orchestrators of precise cytoskeletal dynamic events. In this review, we focus on the prototypical spectraplakin MACF1, a protein scaffold of more than 700 kDa that coordinates the crosstalk between actin microfilaments and microtubules to support cell-cell connections, cell polarity, vesicular transport, proliferation, and cell migration. We will review over two decades of research aimed at understanding the molecular, physiological and pathological roles of MACF1, with a focus on its roles in developmental and cancer. A deeper understanding of MACF1 is currently limited by technical challenges associated to the study of such a large protein and we discuss ideas to advance the field.
Keywords: ACF7; cancer; cytoskeleton; signaling; spectraplakin.
Copyright © 2021 Cusseddu, Robert and Côté.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1: Domains, Interaction Partners, and Tissue-Specific Functions.Methods Enzymol. 2016;569:331-53. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.05.022. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 26778566
-
A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 30;26(7):3204. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073204. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoforms, structures, and functions of versatile spectraplakin MACF1.BMB Rep. 2016 Jan;49(1):37-44. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2016.49.1.185. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 26521939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MACF1, versatility in tissue-specific function and in human disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Sep;69:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 May 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28577926 Review.
-
The cytoskeletal crosslinking protein MACF1 is dispensable for thrombus formation and hemostasis.Sci Rep. 2019 May 22;9(1):7726. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44183-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31118482 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1, a brain tumor oncoprotein (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2024 Dec 3;22(2):15. doi: 10.3892/mco.2024.2810. eCollection 2025 Feb. Mol Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39720461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Profiling Identifies Putative Pathogenic Alterations in NSCLC Brain Metastases.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022 Nov 11;3(12):100435. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100435. eCollection 2022 Dec. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561283 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Compilation of Human SH3 Domains: A Versatile Superfamily in Cellular Signaling.Cells. 2023 Aug 12;12(16):2054. doi: 10.3390/cells12162054. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of MACF1 as a causative gene of generalised epilepsy.J Med Genet. 2025 Jun 24;62(7):484-493. doi: 10.1136/jmg-2025-110699. J Med Genet. 2025. PMID: 40350249 Free PMC article.
-
The role of MACF1 on acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation is involved in Runx2-targeted PI3K/Akt signaling.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Mar;478(3):433-441. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04517-x. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 35857251
References
-
- Bernier G., Pool M., Kilcup M., Alfoldi J., De Repentigny Y., Kothary R. (2000). Acf7 (MACF) is an actin and microtubule linker protein whose expression predominates in neural, muscle, and lung development. Dev. Dyn. 219 216–225. 10.1002/1097-0177(2000)9999:9999<::AID-DVDY1041>3.0.CO;2-O - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

