Hyperbaric Oxygen Improves Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats Probably via Inhibition of Autophagy Triggered by the Downregulation of Hypoxia-Inducing Factor-1 Alpha
- PMID: 33816617
- PMCID: PMC7987430
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6615685
Hyperbaric Oxygen Improves Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats Probably via Inhibition of Autophagy Triggered by the Downregulation of Hypoxia-Inducing Factor-1 Alpha
Abstract
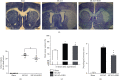
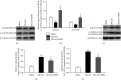
Ischemic stroke, accompanied with high mortality and morbidity, may produce heavy economic burden to societies and families. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore effective therapies. Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) is a noninvasive, nondrug treatment method that has been proved able to save ischemic penumbra by improving hypoxia, microcirculation, and metabolism and applied in various ischemic diseases. Herewith, we fully evaluated the effect of HBO on ischemic stroke and investigated its potential mechanism in the rat ischemia/reperfusion(I/R) model. Sixty Sprague-Dawley male rats were randomly divided into three groups-sham group, MCAO group, and MCAO+HBO group. In the latter two groups, the middle cerebral artery occlusion was performed (MCAO) for 2 hours, and then the occlusion was removed in order to establish the ischemic/reperfusion model. Subsequently, HBO was performed immediately after I/R (2 hours per day for 3 days). 72 hours after MCAO, the brain was dissected for our experiment. Finally, the data from three groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and followed by a Bonferroni test. In this article, we reported that HBO effectively reduced the infarction and edema and improved neurological functions to a certain extent. As shown by western blot analysis, HBO significantly reduced autophagy by regulating autophagy-related proteins (mTOR, p-mTOR, Atg13, LC3B II and LC3B II) in the hippocampus 72 hours after I/R, which was accompanied by inhibiting the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in hippocampus. The results suggest that HBO may improve cerebral I/R injury, possibly via inhibiting HIF-1α, the upstream molecule of autophagy, and therefore, subsequently inhibiting autophagy in the rat model of ischemic stroke.
Copyright © 2021 Cuiting Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

