Performance of Repeated Measures of (1-3)-β-D-Glucan, Mannan Antigen, and Antimannan Antibodies for the Diagnosis of Invasive Candidiasis in ICU Patients: A Preplanned Ancillary Analysis of the EMPIRICUS Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33816643
- PMCID: PMC8002176
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab080
Performance of Repeated Measures of (1-3)-β-D-Glucan, Mannan Antigen, and Antimannan Antibodies for the Diagnosis of Invasive Candidiasis in ICU Patients: A Preplanned Ancillary Analysis of the EMPIRICUS Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: We aimed to assess the prognostic value of repeated measurements of serum (1-3)-β-D-glucan (BDG), mannan-antigen (mannan-Ag), and antimannan antibodies (antimannan-Ab) for the occurrence of invasive candidiasis (IC) in a high-risk nonimmunocompromised population.
Methods: This was a preplanned ancillary analysis of the EMPIRICUS Randomized Clinical Trial, including nonimmunocompromised critically ill patients with intensive care unit-acquired sepsis, multiple Candida colonization, and multiple organ failure who were exposed to broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. BDG (>80 and >250 pg/mL), mannan-Ag (>125 pg/mL), and antimannan-Ab (>10 AU) were collected repeatedly. We used cause-specific hazard models. Biomarkers were assessed at baseline in the whole cohort (cohort 1). Baseline covariates and/or repeated measurements and/or increased biomarkers were then studied in the subgroup of patients who were still alive at day 3 and free of IC (cohort 2).
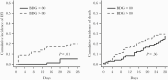
Results: Two hundred thirty-four patients were included, and 215 were still alive and free of IC at day 3. IC developed in 27 patients (11.5%), and day 28 mortality was 29.1%. Finally, BDG >80 pg/mL at inclusion was associated with an increased risk of IC (CSHR[IC], 4.67; 95% CI, 1.61-13.5) but not death (CSHR[death], 1.20; 95% CI, 0.71-2.02).
Conclusions: Among high-risk patients, a first measurement of BDG >80 pg/mL was strongly associated with the occurrence of IC. Neither a cutoff of 250 pg/mL nor repeated measurements of fungal biomarkers seemed to be useful to predict the occurrence of IC. The cumulative risk of IC in the placebo group if BDG >80 pg/mL was 25.39%, which calls into question the efficacy of empirical therapy in this subgroup.
Keywords: (1,3)-β-D-glucan; competing risk models; invasive candidiasis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Kett DH, Azoulay E, Echeverria PM, Vincent JL; Extended Prevalence of Infection in ICU Study (EPIC II) Group of Investigators . Candida bloodstream infections in intensive care units: analysis of the extended prevalence of infection in intensive care unit study. Crit Care Med 2011; 39:665–70. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Rello J, Marshall J, et al. EPIC II Group of Investigators . International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 2009; 302:2323–9. - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M, Garnacho-Montero J, Calandra T, et al. Intensive care medicine research agenda on invasive fungal infection in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 2017; 43:1225–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources