Multidimensional Apathy: The Utility of the Dimensional Apathy Scale in Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 33816664
- PMCID: PMC8015897
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.13147
Multidimensional Apathy: The Utility of the Dimensional Apathy Scale in Huntington's Disease
Abstract
Background: Apathy is a disorder of motivation common to Huntington's disease (HD). Recent conceptual frameworks suggest that apathy is not unitary but consists of discrete subtypes ("dimensions"). Which of the proposed dimensions are preferentially affected in HD, and how these dimensions evolve with disease progression is unknown.
Objectives: The Dimensional Apathy Scale (DAS) separates apathy into Executive, Initiation and Emotional subscales. Using the DAS, we aimed to: 1) Determine the apathy subtypes prevalent in HD; 2) Compare the DAS against a unitary measure of apathy (Apathy Evaluation Scale, AES); 3) Assess the reliability of self- and observer-ratings; and 4) Determine the relationship between the DAS, and disease burden, total functional capacity (TFC) and the AES.
Method: Fifty pre-manifest, 51 manifest-HD, 87 controls, and 50 HD-observers completed the DAS, AES, and TFC.
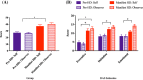
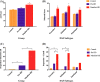
Results: Manifest-HD participants had the highest levels of apathy across all dimensions (30.4% on Executive subscale, 34.8% on Initiation subscale, and 15.2% on Emotional subscale), relative to pre-manifest and control participants. Self- and observer-ratings on the DAS did not differ. Hierarchical regressions across the entire gene-expanded sample showed that scores on the Initiation subscale correlated with AES scores; higher Executive subscale scores were related to higher disease burden; and Emotional subscale scores with lower total functional capacity.
Conclusions: In this first study of the DAS in HD, manifest-HD participants were more apathetic than pre-manifest and control participants across all apathy subtypes. The DAS may be a useful tool for measuring different aspects of apathy in people with HD.
Keywords: Huntington's disease; apathy subtypes; dimensional apathy scale.
© 2021 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
K.A. received a Research Training Scheme Stipend from the Australian Government to conduct this research. There are no further funding sources or conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group . A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 1993;72(6):971–983. - PubMed
-
- Tabrizi SJ, Scahill RI, Owen G, et al. Predictors of phenotypic progression and disease onset in premanifest and early‐stage Huntington's disease in the TRACK‐HD study: analysis of 36‐month observational data. Lancet Neurol 2013;12(7):637–649. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

