Advanced Therapies for the Management of Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33816669
- PMCID: PMC8015898
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.13154
Advanced Therapies for the Management of Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Background: Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome (DDS) is an adverse non-motor complication of dopamine replacement therapy in Parkinson's disease. The current literature on this syndrome is limited, and it remains underdiagnosed and challenging to manage.
Objective: To assess the role of advanced therapies in the management of DDS.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review and identified patients who fit the inclusion criteria for DDS. They were classified according to risk factors that have been identified in the literature, motor and complication scores, intervention (medical or surgical) and outcome. Multivariate analyses were performed to analyze these characteristics.
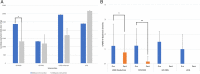
Results: Twenty-seven patients were identified (23 males, mean age of onset: 49 ± 8.8 years). Average levodopa equivalent daily dose was 1916.7 ± 804 mg and a history of impulse control disorders, psychiatric illness, and substance abuse was present in 89%, 70% and 3.7% of the patients, respectively. Overall 81.5% of patients had symptom resolution at follow up, on average 4.8 ± 3.5 years after management, with medication only (7/9), levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel (1/3), deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus (10/13), or globus pallidus pars interna (2/2). Reduction of medications occurred with deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus (P = 0.01) but was associated with a relapse in two patients.
Conclusion: Although the small sample size of some subgroups limits our ability to draw meaningful conclusions, our results did not suggest superiority of a single treatment option. Advanced therapies including deep brain stimulation can be considered in patients with DDS refractory to conservative measures, but outcome is variable and relapse is possible.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; addiction; dopamine dysregulation syndrome; therapy.
© 2021 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease.N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 27;345(13):956-63. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa000827. N Engl J Med. 2001. PMID: 11575287 Clinical Trial.
-
The Persistence of Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome after Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson's Disease.Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2025 May 10. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.70114. Online ahead of print. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 40346925
-
Dopamine dysregulation syndrome: an overview of its epidemiology, mechanisms and management.CNS Drugs. 2009;23(2):157-70. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200923020-00005. CNS Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19173374 Review.
-
Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: meta-analysis of results of randomized trials at varying lengths of follow-up.J Neurosurg. 2018 Apr;128(4):1199-1213. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS16715. Epub 2017 Jun 30. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28665252
-
Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease: restoring the balance of motivated behaviours.Brain. 2012 May;135(Pt 5):1463-77. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws078. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22508959
Cited by
-
Tips and tricks in tremor treatment.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024 Oct;131(10):1229-1246. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02806-x. Epub 2024 Jul 24. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024. PMID: 39043978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Overtreatment Trap: Navigating Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome in Parkinson's Disease.Cureus. 2024 Sep 30;16(9):e70500. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70500. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39479067 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamentals of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease in clinical practice: part 1.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024 Apr;82(4):1-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1786026. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 38653485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single centre prospective study of three device-assisted therapies for Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Jun 29;9(1):101. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00525-w. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 37386050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans AH, Lees AJ. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurol 2004;17(4):393–398. - PubMed
-
- Bonci A, Singh V. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome in Parkinson's disease patients: from reward to penalty. Ann Neurol 2006;59(5):733–734. - PubMed
-
- Bearn J, Evans A, Kelleher M, Turner K, Lees A. Recognition of a dopamine replacement therapy dependence syndrome in Parkinson's disease: a pilot study. Drug Alcohol Depend 2004;76(3):305–310. - PubMed
-
- O'Sullivan SS, Evans AH, Lees AJ. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome. CNS Drugs 2009;23(2):157–170. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

