Aberrant DNA Methylation Involved in Obese Women with Systemic Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 33817084
- PMCID: PMC7874722
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2018-0024
Aberrant DNA Methylation Involved in Obese Women with Systemic Insulin Resistance
Abstract
Background: Epigenetics has been recognized as a significant regulator in many diseases. White adipose tissue (WAT) epigenetic dysregulation is associated with systemic insulin resistance (IR). The aim of this study was to survey the differential methylation of genes in obese women with systemic insulin resistance by DNA methylation microarray.
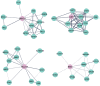
Methods: The genome-wide methylation profile of systemic insulin resistant obese women was obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus database. After data preprocessing, differing methylation patterns between insulin resistant and sensitive obese women were identified by Student's t-test and methylation value differences. Network analysis was then performed to reveal co-regulated genes of differentially methylated genes. Functional analysis was also implemented to reveal the underlying biological processes related to systemic insulin resistance in obese women.
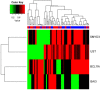
Results: Relative to insulin sensitive obese women, we initially screened 10,874 differentially methylated CpGs, including 7402 hyper-methylated sites and 6073 hypo-methylated CpGs. Our analysis identified 4 significantly differentially methylated genes, including SMYD3, UST, BCL11A, and BAI3. Network and functional analyses found that these differentially methylated genes were mainly involved in chondroitin and dermatan sulfate biosynthetic processes.
Conclusion: Based on our study, we propose several epigenetic biomarkers that may be related to obesity-associated insulin resistance. Our results provide new insights into the epigenetic regulation of disease etiology and also identify novel targets for insulin resistance treatment in obese women.
Keywords: DNA methylation; bioinformatics; insulin resistance; obesity.
© 2018 Shao-Jun Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The epigenetic signature of systemic insulin resistance in obese women.Diabetologia. 2016 Nov;59(11):2393-2405. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4074-5. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27535281 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant DNA methylation associated with Alzheimer's disease in the superior temporal gyrus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):103-108. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5394. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29375678 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative DNA methylomic analyses reveal potential origins of novel epigenetic biomarkers of insulin resistance in monocytes from virally suppressed HIV-infected adults.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jun 28;11(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0694-1. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31253200 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation pattern in visceral adipose tissue differentiates insulin-resistant from insulin-sensitive obese subjects.Transl Res. 2016 Dec;178:13-24.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27477082
-
Potential epigenetic biomarkers of obesity-related insulin resistance in human whole-blood.Epigenetics. 2017 Apr 3;12(4):254-263. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2017.1281501. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 28106509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the epigenetic fabric of type 2 diabetes mellitus: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 22;15:1295967. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1295967. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38323108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between the gut microbiome and DNA methylation patterns in blood and visceral adipose tissue in subjects with different metabolic characteristics.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 1;22(1):1089. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05746-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39617894 Free PMC article.
-
SMYD3: a new regulator of adipocyte precursor proliferation at the early steps of differentiation.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 Apr;48(4):557-566. doi: 10.1038/s41366-023-01450-x. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38148333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A.. Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:4–7. - PubMed
-
- van Dijk SJ, Molloy PL, Varinli H, Morrison JL, Muhlhausler BS.. Epigenetics and human obesity. International journal of obesity (2005) 2015;39:85–97. - PubMed
-
- Kubota T, Kubota N, Kadowaki T.. Imbalanced Insulin Actions in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: Key Mouse Models of Insulin Signaling Pathway. Cell metabolism. 2017;25:797–810. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
