MiRNA-145 Induces Apoptosis in a Gallbladder Carcinoma Cell Line by Targeting DFF45
- PMID: 33817087
- PMCID: PMC7874708
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2018-0027
MiRNA-145 Induces Apoptosis in a Gallbladder Carcinoma Cell Line by Targeting DFF45
Abstract
Bakcground: We measured expression of miRNA-145 in gallbladder carcinoma and its influence on propagation, invasion, and apoptosis of gallbladder carcinoma cells in vitro.
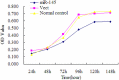
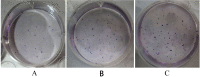
Methods: miRNA-145 expression was compared between normal gallbladder epithelial cells and GBS-SD (gallbladder series) cells using miRNA chip technology. Propagation, apoptosis, and invasion properties of each cell group were tested using MTT, a clone-formation assay, flow cytometry, Western blot, and Transwell assays.
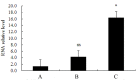
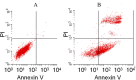
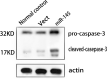
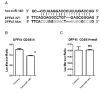
Results: Expression of miRNA-145 was observed to be down-regulated and GBC-SD cell clones transiently transfected with hsa-miRNA-145 were substantially reduced compared with controls (p<0.01). We observed that GBC-SD cells transfected with hsa-miRNA-145 and double-positive (Annexin V and PI) for apoptosis were more numerous than controls. Moreover, GBC-SD cells over-expressing miRNA-145 had significantly greater expression of apoptosis-related protein, caspase-3. A Transwell assay confirmed that GBC-SD cells over-expressing miRNA-145 that migrated to the lower chamber were fewer compared with controls. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression was measured using dualluciferase reporter assays and data show that miRNA-145 facilitates the inhibition of GBC-SD cell growth and invasion while inducing apoptosis by targeting DFF45.
Conclusion: Thus, we speculate that miRNA-145 facilitates inhibition of GBC-SD cell growth and invasion while inducing apoptosis by targeting DFF45; however, miRNA-145 does not directly affect the GBC-SD cell cycle.
Keywords: DFF-45; MTT; clone formation assay; flow cytometry; miRNA-145.
© 2018 Yuan Yuan et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Curcumin induces apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cell line GBC-SD cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Jun 26;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-64. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23802572 Free PMC article.
-
Bmi-1 in gallbladder carcinoma: Clinicopathology and mechanism of regulation of human gallbladder carcinoma proliferation.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1365-1371. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10408. Epub 2019 May 28. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423199 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin enhances the chemosensitivity of GBC-SD cell line to doxorubicin through arresting the cell cycle to S phase rather than through the P53/Bax-depended apoptosis way in vitro.Hepatogastroenterology. 2009 Sep-Oct;56(94-95):1253-60. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19950772
-
Inhibitory effect of norcantharidin on the growth of human gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells in vitro.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007 Feb;6(1):72-80. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007. PMID: 17287171
-
Lupeol induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion in gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells by suppression of EGFR/MMP-9 signaling pathway.Cytotechnology. 2016 Jan;68(1):123-133. doi: 10.1007/s10616-014-9763-7. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Cytotechnology. 2016. Retraction in: Cytotechnology. 2022 Dec;74(6):681. doi: 10.1007/s10616-022-00550-2. PMID: 25037728 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs as potential biomarkers of gallbladder cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jun;25(6):1489-1511. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-03056-7. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36576705 Review.
References
-
- Jorge AS, Avissai AV, Humberto CO, Roberto HG.. The Precursor Lesions of invasive gallbladder carcinoma. Hyperplasia, atypical hyperplasia and carcinoma in situ. Cancer. 1980;MM45:919–927. - PubMed
-
- Quan Z.. Advances in gallbladder carcinoma - related genes and tumor markers. Chin J Practic Surg. 2003;23(10):638–640.
-
- Goldin RD, Roa JC.. Gallbladder cancer: a morphological and molecular update. Histopathology. 2009;55(2):218–229. - PubMed
-
- Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR, Jacks T.. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39(5):673–677. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
